Over recent years, customers have changed the way they interact with banks. Ever since digital-savvy fintechs and neobanks came into the picture, digitization has become the need of the hour for banks. Banks must approach digitization in a progressive fashion by focusing on aspects that make for a seamless customer experience to retain their position as market leaders.
We will soon see banks emerge as digital-first financial institutions as they leverage their network of distribution channels backed with the trust that customers hold in them.
The last two years have, without a doubt, driven the focus of banks on digitization and customer-centricity. According to a McKinsey report, 75% of customers have tried different brands since the pandemic started. Out of these, 60% are expected to adopt new brands and stores into their post-pandemic lives and routines.
The Evolution of Digital Banking
The evolution of digital banking has been a remarkable journey, transforming the way people manage their finances and interact with financial institutions. From the early days of online banking to the current era of mobile banking and digital-only banks, the industry has undergone significant changes. Advances in technology, changing consumer behavior, and the need for financial institutions to stay competitive have driven this transformation.
One of the key trends in online banking is the shift towards mobile banking. With the increasing use of smartphones, mobile banking has become a convenient and accessible way for people to manage their finances on the go. Mobile banking apps have become essential tools for banks to provide their customers with a seamless and user-friendly experience.
Another significant trend in digital banking is the emergence of digital-only banks. These banks operate entirely online, without any physical branches, and offer a range of financial services, including bank accounts, loans, and investments. Digital-only banks have disrupted the traditional banking model, offering lower fees, higher interest rates, and a more personalized experience.
The digital banking landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies and innovations emerging all the time. The use of artificial intelligence, blockchain, and biometric authentication are just a few examples of the technologies that are transforming the industry. As the digital banking landscape continues to evolve, it’s essential for financial institutions to stay ahead of the curve and adapt to changing consumer needs and expectations.
Today, customers seek empathy, loyalty, and emotional connection from brands. Most customers agree that it is high time for businesses to reconsider how they operate and contribute to society. Hence, banks will now have to widen their perceptions and enrich the digital experience with an emotional connection. Read on to learn about ten digital banking trends that are thriving even in 2024!
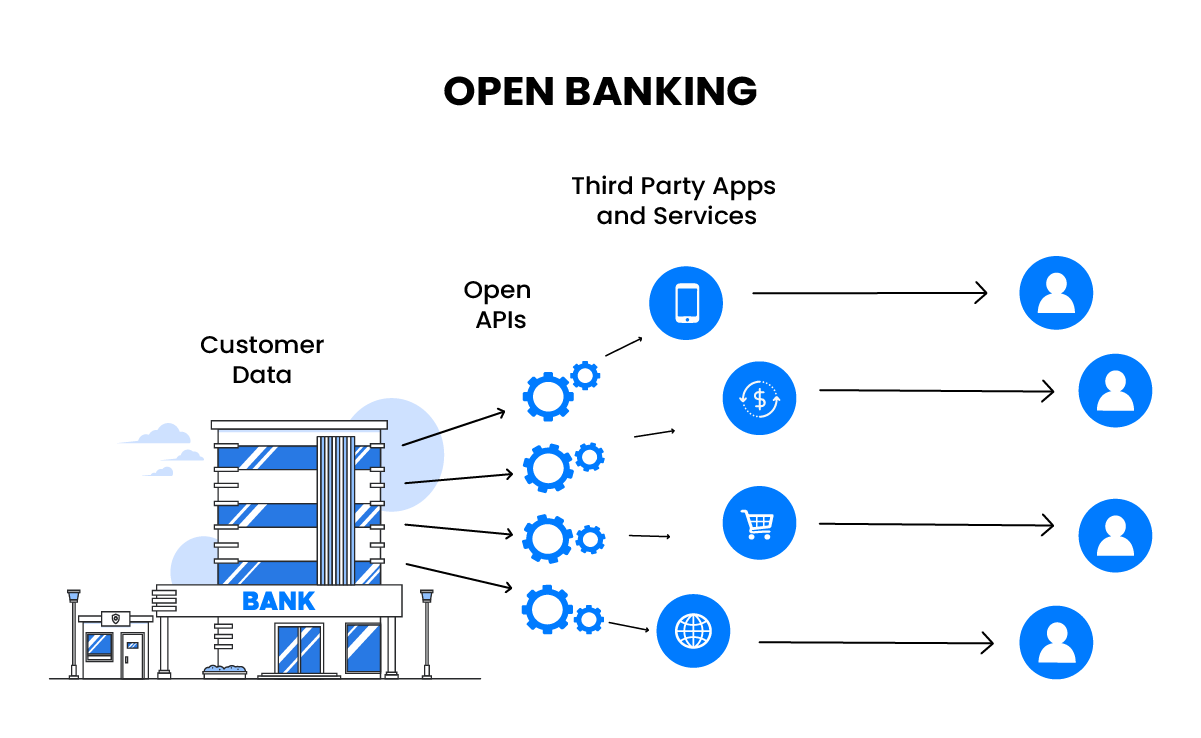
1. Open Banking
While an API economy is already underway in the banking arena, it certainly shows great potential in creating new and improved financial services. Therefore, making it one of the top banking trends across the world! Simply put, open banking allows banks to share financial data with other fintechs and tech-forward companies through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) subject to the customer’s consent. This will enable banks to collaborate with other financial institutions within the banking industry, and help customers access a range of financial services on a single platform.
2. Customer Experience is Everything!
Whether it’s filling out a loan application form, reaching out to customer helplines, or even walking into their bank branch, a consistent banking experience is the need of the hour. Customers want to feel understood and are looking to financial institutions to address their financial aspirations in the best possible way. This calls for banks to be more intuitive, introduce personalization, be data-driven, and anticipate their needs through the use of a mobile banking app. Banks that integrate this perspective in their digitization journey will continue to hold a strong market position.
3. Bridging Customer Needs and Expectations
The banking system, be it traditional or modern, can leave numerous gaps between what the customer expects and what the bank can provide. If the difference is greater, there is a high chance that the customer will drop the bank altogether. A couple of decades ago, when only a handful of banks operated, it was difficult for customers to switch banks. Currently, digitization has made it easy for customers to switch banks and weigh options that best suit their financial needs, including the ease of managing a bank account through digital means. For financial institutions to succeed in a competitive market, they need to address these gaps.
The gap between customer expectations and services of financial institutions exists at various levels, such as:
- A culture gap exists when the top management is not customer-focused. This situation prevents employees from giving customers the best possible experience.
- The feedback gap happens when the organization does not collect feedback or fails to incorporate it into the business processes.
- The design gap is when products and services are of low quality. Bridging the design gap requires careful customer-centric planning. The execution gap is not being able to provide a satisfactory UX.
- There is also the value gap where the design of the products and services do not meet the customers’ expectations.
- And finally, there is the emotional gap, where customers don’t feel understood by their banks.
When creating digital banking products and solutions, it’s pivotal to address these gaps. Some banks are realizing its significance and are open to collaborating with fintech startups.ealizing its significance and are open to collaborate with fintech startups.
4. Building an Emotional Connection
Building an emotional connection with the customer is becoming increasingly essential. In 2022, fintech companies and digital banks built personalized experiences for customers based on the connections established with their customers. Now, it’s not just about using their “first name” in their fintech marketing strategies, but keeping the entire digital experience personalized.
When it comes to digital experiences, banking applications certainly have a long way to go. For instance, e-commerce platforms address the needs of the users in the best way possible by being data-driven, understanding behavioral patterns, and other such cues to humanize the experience. Banking applications must benchmark the UI/UX these platforms provide to build a similar customer experience and emotional connection with customers. Services like N26 and Mint are examples of apps that take personalization to the next level; Abe AI integrated banking services with Google Home to provide a more convenient banking experience!
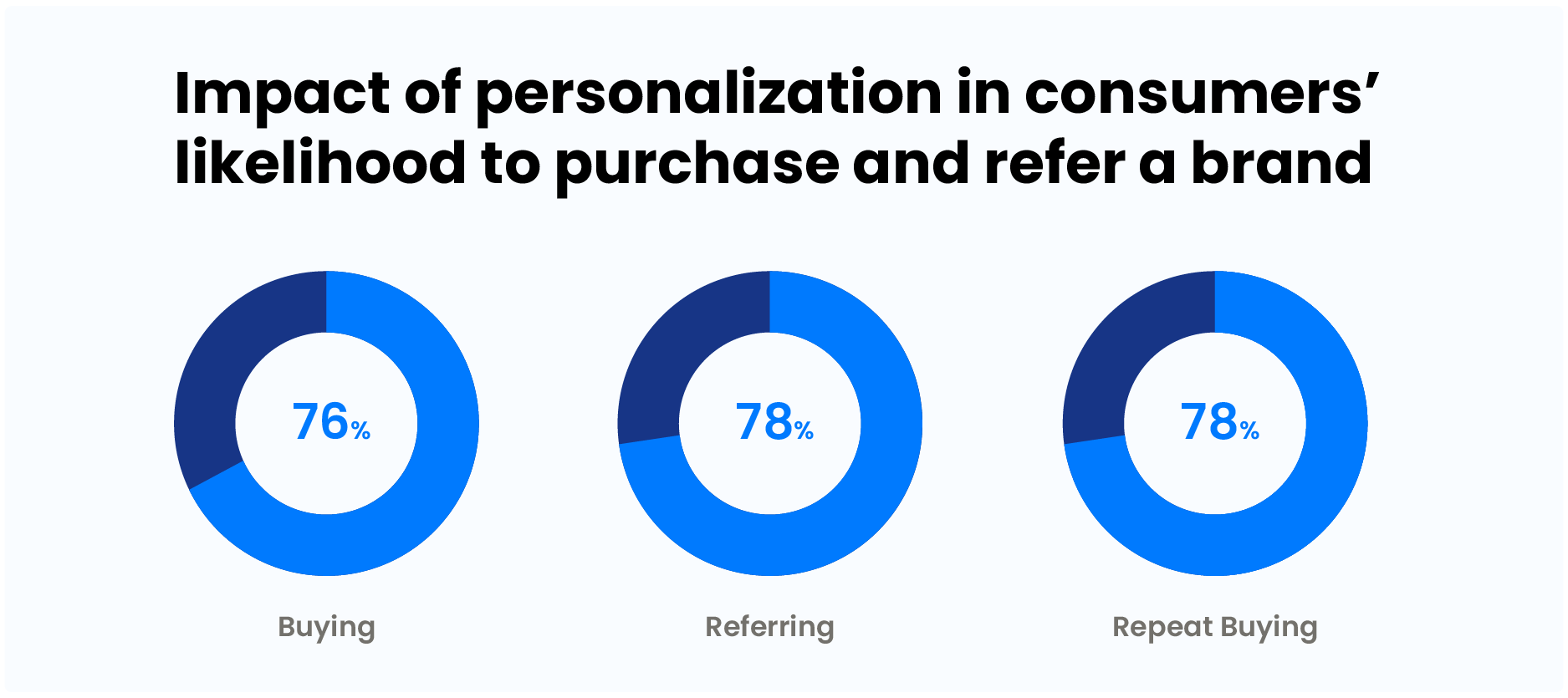
5. Measuring Modern Metrics
With customer experience as the primary focus, most financial institutions will shift to experience-driven metrics to evaluate their performance. The key performance indicators of digital banking products will assess how competently they’re engaging with customers. The metrics will not just look at the operational efficiency but also how comfortable the customers are using them. The new metrics will consider user feedback which includes user comments, ratings, and recommendations.
Financial institutions can switch to these new metrics without making many new investments. The metrics that financial institutions can evaluate include app store ratings, net promoter scores, customer lifetime value, reasons why most customers contact support, app retention and switch rates, active customer volume, and other such parameters, including the integration of money market accounts to enhance user experience.
6. Automation and the Shift to EQ
Emotional intelligence has become a non-negotiable requirement for the banking sector. While banks and financial institutions have primarily marketed their IQ, EQ is slowly becoming a salient part of the equation. Newer technologies, such as artificial intelligence, are enabling fintech institutions to be less robotic. For example, BELLA is a banking platform that shows how brands can integrate EQ into banking. It acts as a conversational banking platform with a focus on fostering a community.
7. Developing a Consistent Ecosystem
An issue with modern digital banking systems is the lack of consistency. Legacy banks experience digitization in phases. It has led to a fragmentation of user experience across the channels in their ecosystem. Visual elements across apps and websites look and behave differently. The Internet banking website, the apps, and the ATMs: each have their distinct interface that lacks parity. For example, the State Bank of India has multiple apps for investment, payments, and card management. They even have an app that unifies all these features. Each of them has a different UI and design system. This UX is also completely different from that of the website.

Customers expect all channels to provide a consistent experience when using digital banking. A unified experience will help establish a smooth transition as the customer switches between different banking platforms.
8. Cybersecurity and Fraud Detection
In the digital banking landscape, cybersecurity and fraud detection have become paramount. As financial institutions increasingly rely on digital channels, the risk of cyber attacks and fraud has surged. To safeguard customers’ sensitive information and prevent financial losses, robust security measures are essential.
One of the leading trends in cybersecurity is the adoption of biometric authentication. This technology leverages unique physical characteristics, such as fingerprints or facial recognition, to verify identities and prevent unauthorized access to bank accounts. Biometric authentication has gained popularity for its secure and convenient approach to customer verification.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are also revolutionizing cybersecurity. These technologies analyze patterns and anomalies in customer behavior to detect and prevent cyber attacks. AI-powered systems can identify and flag suspicious transactions, significantly reducing the risk of fraud and financial losses.
Beyond technology, financial institutions must invest in customer education and awareness programs. Providing customers with tips and advice on staying safe online, along with resources and support for recovering from cyber attacks, is crucial in the fight against cyber threats.
9. Leveraging Banking-as-a-Service
Banking-as-a-Service is a partnership model where banks allow fintechs and other non-banks to access their core systems through APIs and webhooks.
For example, an airline can offer customers a branded debit card or other digital banking services that customers can use to book tickets to win loyalty points. In this case, the airline doesn’t require a banking license because it interacts with the bank’s systems via APIs allowing customers to access a range of digital banking services via the airline’s app or website.
Banking-as-a-Service presents a huge market opportunity for banks because they can tap into new revenue streams, cater to a larger set of customers, develop a better tech stack in a cost-effective fashion, and establish their relevance with a restructured market proposition.
There are companies that offer BaaS platforms for users worldwide. They either fall under the fintech or retail BaaS companies. Some of them include Cambr and Solaris Bank.

10. Increasing Collaborations with Fintechs
Traditional banking institutions are increasingly partnering with fintech companies to integrate digital processes in their businesses. Traditional banks are often too big to be digitized in a short span of time. Phased digitization has also caused fragmentation. Hence, banks can partner with fintech companies and startups to bring innovation and convenience to their customers. The partnerships can be for various reasons.
For instance, Commerzbank partnered with IDnow to help verify customers over video calls.

FidorBank had partnered with CurrencyCloud for its e-payment system. Similarly, Bankia collaborated with Euro Bits to provide invoicing services for SMEs.

The idea of co-operation over competition is gaining more prominence with strategic partnerships between financial institutions.
Bonus – A Few More Trends You Can Consider!
Here are a few more trends to watch. Embrace these, and you’ll find new opportunities and a deeper connection with your audience!
11. Embedded Finance and Central Bank Digital Currencies
Embedded finance and central bank digital currencies are two emerging trends in digital banking that are set to transform the industry. Embedded finance refers to the integration of financial services into non-financial platforms and applications. This allows customers to access financial services, such as payments and loans, without having to leave the platform or app they are using.
Central bank digital currencies, on the other hand, are digital currencies issued by central banks. These currencies are designed to provide a secure and efficient way for people to make payments and transfer money. They have the potential to disrupt the traditional banking model, offering a faster, cheaper, and more secure way for people to manage their finances.
One of the key benefits of embedded finance is that it provides customers with a seamless and convenient experience. By integrating financial services into non-financial platforms and applications, customers can access the services they need without having to navigate multiple websites or apps. This can also help to increase financial inclusion, by providing access to financial services for people who may not have had access to them before.
Central bank digital currencies also offer a range of benefits, including increased security and efficiency. These currencies are designed to be secure and resistant to cyber attacks, reducing the risk of financial losses. They also offer a faster and cheaper way for people to make payments and transfer money, reducing the need for intermediaries and increasing the speed of transactions.
Overall, embedded finance and central bank digital currencies are two exciting trends in digital banking that have the potential to transform the industry.
12. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
Another big trend that has started to take off in digital banking is the rise of Decentral Finance (DeFi).
As consumers and businesses want more control over their transactions, DeFi platforms are becoming an alternative to traditional banking. By using blockchain, these platforms allow peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and trading without intermediaries. This means users get to control their assets and potentially lower fees and faster transactions.

Another part of this trend is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in DeFi applications to enhance customer experience. AI tools are being used for risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized financial advice so users can navigate complex financial products more easily. These also streamline operations and build trust with consumers who are wary of the security and reliability of decentralized platforms.
Finally, regulatory developments are also shaping DeFi. As governments and financial institutions start to set clear guidelines for decentralized finance, this will encourage more users to join who were previously hesitant. By creating a safer and more regulated environment, the DeFi trend will accelerate and open up new opportunities for innovation in digital banking and how we manage our finances.
13. Sustainable and Inclusive Banking Industry
Today, customers expect more from their favorite brands. For instance, people want to be associated with institutions that care for the society and environment. Most new-age customers today do not hesitate to contribute to a cause. Moreover, they resonate with institutions that imbibe these values.
It has provided financial institutions with an opportunity to rethink their purpose, modify their mission statement, and make the digital banking experience more personal, empathetic, and understanding.
For example, the green fintech initiative: a collaboration between fintech and climate tech, makes banking sustainable. Banking solutions like Tomorrow and Bunq promise to make digital banking more viable.
Final Thoughts
Final Thoughts
Customers expect banks and financial institutions to have their back, and understand their financial goals and aspirations. The need for digitization has accelerated irrespective of the industry being discussed.
LeadSquared helps brands connect with their customers in a more efficient way. Explore its low-code/no code sales efficiency solutions for banking and financial services to thrive in the modern world of financial services!
FAQs
What is digital banking?
Digital banking is the availability of banking services online, therefore making way for paperless banking services.
What are the advantages of digital banking?
While there are many advantages of digital banking, the key takeaways are convenience, ease of use, accessible banking, and personalized services.
What are the Top 3 banking trends?
Besides the top digital banking trends discussed in the article, here’s a look into the Top 3 banking trends:
1. Core modernization
If banks need a market share of the new-age banking, they must transcend from legacy infrastructure and modernize their core. This will enable them to create digital-first customer experiences, tap into Banking-as-a-Service, embedded finance and much more.
2. Hyper-personalization
Banks that align their propositions to their customer’s needs will be a front runner. Banks must be data-driven and leverage technology like AI to truly introduce hyper-personalization across customer touchpoints.
3. Rise of no-code/low-code solutions
Financial institutions are adopting solutions that enforce central decisioning by eliminating silos and building a connection between IT and other business departments. With a new digital environment, IT departments no longer have to intervene for every business aspect. These solutions enable quicker deployment, easy integration, decreased operational costs, higher agility, and other such advantages.
Further reading:









