How do you predict your brand’s ability to grow?
The quick answer is—by tracking your Return on Sales or ROS.
We all want to have our sales numbers as high as possible. But does everyone achieve it?
Surprisingly, only 24.3% of salespeople surpassed their quota in 2021, as per Sales Insights Lab. What does it mean? And what does it have to do with ROS?
- First, it means that most companies are not able to effectively increase their ROS.
- Second, the sales reps who did manage to exceed their quota are significantly small in number.
This brings us to the natural conclusion: increasing return on sales is not easy.
So, what’s the solution?
Well, according to high-performing reps, the secret to higher ROS lies in the customer-centric service.
LinkedIn’s State of Sales 2021 report found:
- Top performers-those who met their quota by 125% or more-are likely to put their customers first. 72% of the top performers chose the ” always ” option when asked if they put the buyer first.
It makes complete sense, but are these results visible to customers?
The short answer is- no.
Barely 23% of buyers believe that sellers put them first. As a result, ROS is generally lower than most of us would like it to be.
Top performers do make a difference. But the answer to increasing ROS is far more complex. Before we explore how you can increase your return on sales, let’s define it first.
What is Return on Sales?
ROS or Return on Sales is an important sales KPI that displays how much profit you earn per dollar of sales. It is used to assess a company’s operational effectiveness.
For example, imagine your company made $60,000 in revenue and spent $30,000 this year.
To calculate your ROS, you must first find the profit you made. To do this, subtract your sales from your expenses, i.e., $60,000-$30,000. This results in a profit of $30,000. Next, divide this figure by the total sales or revenue, which is $60,000.
This gives us a value of 0.5. To calculate your ROS percentage, multiply this value by 100. Overall, the ROS percentage will be 50%.
For each dollar in sales, that percentage reflects how much profit you make in cents. Your ROS would be 50 cents per dollar in this case.
Return on Sales Formula
Calculating ROS is fairly simple. You can use the following formula to calculate the return on sales.

Where, Profit = Revenue – Expenses
Note, you can calculate the ROS on a monthly, quarterly, or yearly basis. Just ensure that you’re entering the Profit and Revenue numbers for the same period of time.
A rising ROS shows that a business is growing. A declining ROS, on the other hand, could indicate approaching difficulties.
We use ROS to compare current and future period estimates to past period calculations. This enables a business to study trends. It also indicates your company’s operational efficiency.
Comparing one company’s ROS percentage to that of a competitor is highly valuable. One of the most telling indicators of a company’s overall profitability is its return on sales. The return on sales ratio is vital to creditors and investors.
It gives a clear image of a company’s ability to repay loans, reinvestment possibilities, and dividend prospects.
The return on sales ratio is one of the most reliable measures used by businesses to assess their annual performance. But some businesses consistently rely on the ROS ratio. Let’s look at them.
Return on Sales Examples
1) The Automotive sector
In 2021, the automotive manufacturing sector’s size was at 2.7 trillion dollars. In 2022, the size is forecast to reach a value of 2.8 trillion dollars.
Investors are constantly looking for ways to judge whether a manufacturer is worth their money. This makes the return on sales ratio an ideal way to forecast manufacturer growth.
The return on sales from automotive dealers in 2021 was 7.2%. The return on equity, a measure of return on investment, was 29.1%. Investors can confidently invest their assets only after they know these figures. Measuring and analyzing these ratios are vital to gaining trust from investors.
2) The print and publishing sector
There’s a constant refrain among the internet-age Gen Z and the millennial crowd about how the print is dying. But the industry’s return on sales figures points to the opposite.
The print and publishing sector had a return on sales percentage of 7.5 in 2021. Alongside this, the return on equity was at 5.5%. The 2022 return on equity shows a rising number which currently sits at 12.2%.
It could be because the print sector is better adapting to the online format. In contrast, it could also mean we’re witnessing a resurgence in the consumption of print media. If you’re in the print and publishing sector, it’s a good time to get investors on board.
3) Air transport
The air transport industry took a major hit in 2020 due to the Covid 19 pandemic. This led to the return on sales figures falling to an all-time low of – 41.7%. By 2021 these figures had a significant increase, bouncing back to a solid 2.5%.
Return on sales depends on multiple factors, and this example displays exactly that. If your sector is experiencing an overall decline in sales, increasing your ROS is a real challenge.
Your profit margin can drop significantly depending on various circumstances. This is why it is crucial to monitor and keep track of your return on sales.
But wait, what is the difference between the return on sales and your profit margin? Let’s figure out how return on sales differs from your profit margin.
Return on Sales versus Profit Margin
Some points to note while measuring your return on sales are:
- It is a direct measure of your business’s operational efficiency.
- It does not include any interest or taxes when we calculate it.
In contrast with the profit margin, we calculate ROS by:
- Taking into account both taxes and interest when we calculate it.
- It is a direct measure of how much profit your business gains in a quarter/year.
Although many people use these terms synonymously, they are very different. An example of measuring your profit margin would be:
- Let’s say, you earn $10,000 by selling products worth $5000. Your profit comes up to $5000, this is after you take into account your taxes and interest.
- Next, divide this figure by your total revenue to get 0.5.
- After this, you multiply the value by 100 to get a profit margin of 50%.
- Both formulas remain the same, the only difference lies in the numerator. As profit margin measurements require you to calculate with taxes and interest in mind.
With that, we come to the final section of this article, how do you increase your return on sales?
3 Practical ways to increase your return on sales
1) Invest in the right tech
Investing in a solution that works in your favor can be a game-changer. LinkedIn’s 2021 State of Sales report found that technology is at the core of fostering trust. Sales technology, in particular, is a critical component in establishing trust. Let’s look at some figures that explain this in more depth:
- 77% of sellers claim they want to increase their spending on sales intelligence tools.
- Furthermore, 54% of sellers claim sales tools help them develop stronger connections with customers.
- Another 54% of salespeople said that using sales tools helps them win more deals.
The clear step to improving your ROS is to make selling easier. Investing in any tool can seem expensive at first. But these tools offer a highly beneficial return on investment.
These are the best tools to invest in if you’re wondering what you should buy:
- A CRM system
- A sales engagement tool
- Sales intelligence software
A CRM solution brings the most benefits to sales reps on this list. If you’re a sales-led organization, investing in sales CRM makes more sense. It will help organize leads and manage sales processes effectively. One such great sales CRM is LeadSquared.
Sales intelligence or engagement software tends to be more niche and specific. For instance, if your reps are struggling with only prospecting, then something like LeadFeeder or LinkedIn’s Sales Navigator would be a better option.
Overall, improving your ROS takes time and effort, with the right investment though you’ll see improvements sooner than later.
2) Keep customers at the core of your business
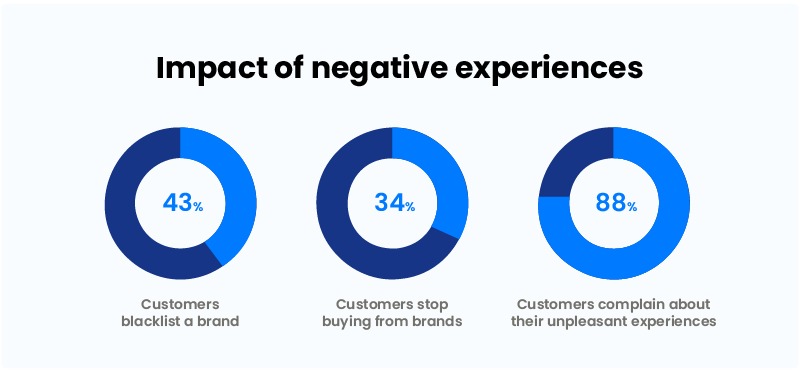
Creating positive customer experiences will automatically push your ROS to greater heights. The best way to go about this is by focusing on retention. For instance, statistics show:
- One negative experience led to nearly 43% of consumers blacklisting a brand.
- After just one unpleasant encounter, more than 34% of customers claim they would never buy from a brand again.
- More than 88% of customers complain about their unpleasant experiences.
- Around 59% of people will inform their friends and family of their negative experience.
- Only 35% of people will call a brand to allow them to fix the problem.
Investing in creating meaningful customer relationships is essential in current times. Customer loyalty can be hard to attain and sustain over time. Creating positive customer experiences from the get-go is necessary to increase your ROS.
Providing sales reps with intensive and informative training is the first step. But the second and more vital step is to maintain a high level of accountability and transparency.
Your return on sales may not shoot up immediately. But I can guarantee a good level of stability on your ROS figures in the long run.
3) Competitive pricing for a complete package
The final and most obvious method to increase your ROS is to increase product cost. However, research beforehand to make sure you’re not pricing yourself out of the market.
You do not have to be pricing the same as your competition all of the time. Make sure you advertise any advantages you have, such as a warranty or excellent customer service.
It provides adequate justification for your buyers to pay the higher price for your product. Even a ten-cent increase in the price of an item that you sell 10,000 copies monthly will raise your profit by $1,000.
It might seem daunting to carry out at first. But the increase will be gradual, and your product value will justify it. You can also strive to lower your inventory costs.
Check with your vendors to see if you can get any discounts. If discounts aren’t available, try to lower the price of inventory. Consult other suppliers to determine whether switching suppliers may result in a discount. Even the tiniest reductions add up to significant profit gains.
With that, we come to the end of this section. Let’s get right into some points to remember and FAQs.
Key Takeaways
Return on sales is a useful metric that you can use in a variety of situations. It’s critical to have a picture of your brand as a business owner. You should know what ROS is and how to measure it if you wish to know how effectively you’re turning over revenue. The key points to note from this post are:
- ROS is highly dependent on the industry within which you operate. Your ROS can decrease or increase as a result of changing supply and demand.
- Aiming to increase your ROS is a great idea. But the step before that is to ensure you can maintain your existing ROS. Focus on retaining customers first, then move on to acquisition.
- Measuring your return on sales can help you keep track of your company’s efficiency. But it is not the only metric you need to measure. Metrics like customer lifetime value are equally important to company growth.
FAQs
What is a good return on sales?
An ROS between 5-10% is what most reports claim to be a good return on sale. But the better idea would be to check your industry-specific ROS benchmarks. For instance, the publishing industry’s ROS in 2021 was 7.5%. In contrast, during the same year, the water transport sector had an ROS of -11%. In general, a positive integer on your return on sales ratio is a favorable sign.
What does ROS mean in business?
Return on Sales is a financial metric that measures how well a firm can create operating profit from its revenue. We typically use it to evaluate the performance of an organization. We do this by determining what percentage of revenue ultimately results in profit for the firm. It indicates whether or not the company’s operations are progressing to their full potential.
Is sales return an expense?
We generally do not consider any sales returns as an expense. But, sales returns do reduce our income or earnings significantly. As most of us are aware, an expense indicates spending some amount of money. Sales returns on the other hand are a loss of earnings. It counts as a loss in your revenue but is not an expense.
Does a low return on sales indicate a weak company?
A low return on sales does not indicate a weak business. Return on sales is merely one aspect of a company’s overall performance. Moreover, companies should use ROS only within their industry benchmarks. A declining return on sales is a cause for concern. But there are always ways to increase your ROS. Explore the reasons for your low ROS and figure out how to overcome them.
What’s the difference between ROS and operating margin?
There is a distinction between the two, despite the fact that they are frequently used interchangeably. The numerators are the difference between ROS and operating margin. We calculate return on sales using profits before interest and taxes (EBIT). EBIT vs. operational income is the most significant distinction between these two ratios. EBIT is a non-GAAP- Generally Accepted Accounting Principles measure that we use for ROS. Operating income, which is a GAAP statistic, is what we use to calculate the operating margin.








![How to Calculate Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)? [Formula and Tips to Improve It] 3 Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)](https://www.leadsquared.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/06/Customer-Lifetime-Value-CLV-80x80.png)
![Calculate Net Sales [Free Calculator, Formula and Examples] 4 How to calculate net sales - formula and free online net sales calculator](https://www.leadsquared.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/How-to-Calculate-Net-Sales.jpg)