“You cannot improve what you cannot measure.”
Defining KRAs, or Key Result Areas, for your sales managers gives them focus and direction. It enables them to align their efforts with the overall sales strategy and prioritize tasks accordingly.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the roles and responsibilities of a sales manager, how you can quantify them and track progress. We’ll also share a sample OKR sheet for sales manager that you can upload in DarwinBox or any other HRMS tool you use.
An Overview of Roles and Responsibilities of a Sales Manager
Sales managers are the backbone of any sales team. They play a crucial role in driving revenue, developing talent, and ensuring the smooth operation of the sales engine. Here’s an overview of their key roles and responsibilities:
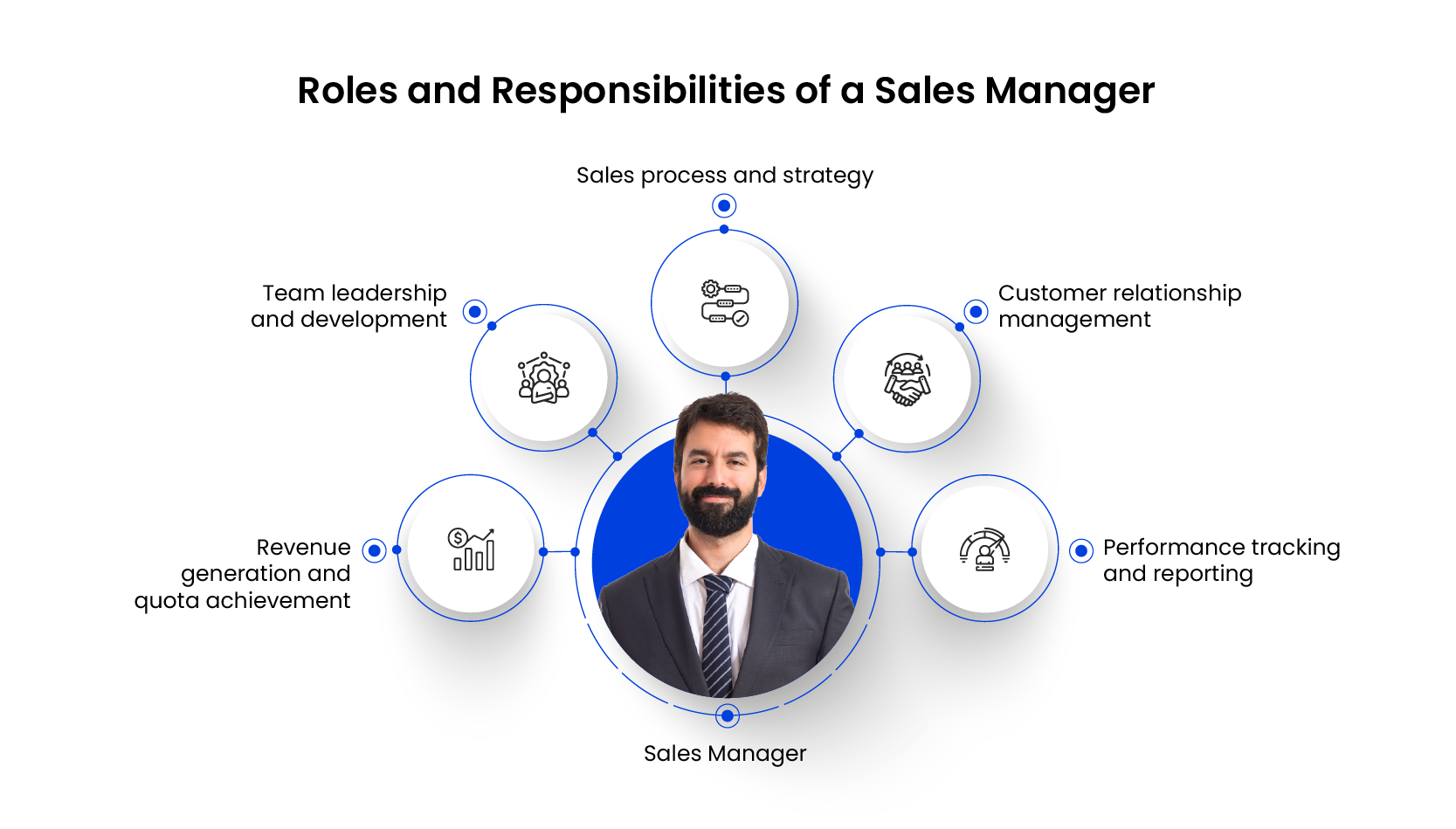
1. Revenue generation and quota achievement
- Set sales targets for the team and individual team members.
- Develop and implement sales plans to achieve set quotas.
- Monitor sales performance, identify roadblocks, and adjust strategies as needed.
- Motivate and coach the sales team to meet and exceed their targets.
2. Team leadership and development
- Recruit, hire, and onboard talented salespeople.
- Provide ongoing training and mentorship to develop individual skills and sales expertise.
- Foster a collaborative environment that promotes teamwork and knowledge sharing.
- Motivate and inspire the team to achieve their full potential.
3. Sales process and strategy
- Implement a clear and effective sales process for the team to follow.
- Analyze customer needs and develop targeted sales strategies to win deals.
- Conduct competitor analysis to understand market dynamics and develop a competitive edge.
- Continuously monitor and improve the sales process for efficiency and effectiveness.
4. Customer relationship management
- Work with customer success teams to ensure customer satisfaction and retention.
- Develop and maintain strong relationships with key clients and accounts.
- Identify new business opportunities and expand the customer base.
- Address customer concerns and ensure a positive brand experience.
5. Performance tracking and reporting
- Track and analyze key sales metrics.
- Generate reports to measure team performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Regularly communicate sales performance to the team and upper management.
- Utilize data-driven insights to optimize sales strategies and resource allocation.
Sales managers wear many hats. They are leaders who set direction, coaches who develop talent, and strategists who drive results. Their success hinges on their ability to combine leadership skills, sales expertise, and data-driven decision making.
15 Result-oriented KRAs of Sales Managers
1. Revenue growth (Focuses on overall financial performance)
This KRA emphasizes the sales team’s contribution to the company’s financial goals by increasing total revenue generated.
Example: Achieve a 15% increase in year-over-year sales for the assigned team.
Success metric: Track total revenue generated by the team compared to the previous year.
2. Quota attainment (Holds teams accountable for specific targets)
This KRA ensures the sales team achieves sales targets set for a specific period.
Example: Ensure the sales team achieves 100% of its quarterly quota.
Success metric: Monitor the team’s progress towards the quota throughout the quarter. Analyze reasons for shortfalls and adjust strategies as needed.
3. New business acquisition (Expands customer base and market reach)
This KRA focuses on acquiring new clients and expanding the company’s customer base.
Example: Secure 10 new client contracts with a minimum value of $10,000 each.
Success metric: Track the number of new clients acquired and the total value of those contracts.
4. Sales pipeline management (Ensures a steady flow of qualified leads)
This KRA emphasizes maintaining a healthy pipeline with qualified leads at various stages, ensuring a consistent flow of potential deals.
Example: Maintain a sales pipeline with a value of $2 million, with at least 30% of leads in the final stages of the sales cycle.
Success metric: Monitor the size and quality of the sales pipeline. Analyze conversion rates at each stage to identify areas for improvement.
5. Coaching and development (Invests in building a skilled sales team)
This KRA focuses on the sales manager’s ability to coach and develop individual team members, enhancing their skills and knowledge.
Example: Conduct one-on-one coaching sessions with each team member bi-weekly to develop their sales skills, focusing on objection handling techniques.
Success metric: Track the number of coaching sessions conducted and measure improvement in individual sales performance metrics.
6. Team motivation and engagement (Creates a positive and productive work environment)
This KRA fosters a positive and motivated sales team through effective leadership and recognition programs.
Example: Implement a recognition program to celebrate individual and team achievements, awarding bonuses for exceeding quotas.
Success metric: Monitor team morale through surveys and track key metrics like turnover rate and absenteeism.
“Something as simple as a pizza party brings the team together. Sales is competitive, which can drive team members apart, but we’re all in the same boat, so being supportive can help every individual perform better.”
– Arjun Mathur, Associate Director, Emeritus
7. Customer eetention (Prioritizes building long-term customer relationships)
This KRA focuses on retaining existing customers and minimizing customer churn.
Example: Achieve a customer retention rate of 90% by implementing a strong customer success program that provides ongoing support and value.
Success metric: Track the percentage of customers who continue business with the company year over year.
8. Sales activity metrics (Tracks effort and identifies areas for improvement)
This KRA focuses on monitoring the sales team’s activity levels, such as calls made and emails sent, to ensure sufficient effort is being directed towards lead generation.
Example: Ensure the sales team completes an average of 50 calls and sends 20 personalized emails per day, tracking these metrics within the CRM software.
Success metric: Track activity levels through CRM software and analyze their correlation with sales results.
9. Lead conversion rate (Measures effectiveness of sales process)
This KRA focuses on the efficiency of converting qualified leads into paying customers.
Example: Increase the conversion rate from qualified leads to closed deals by 10%.
Success metric: Track the percentage of qualified leads that convert into paying customers.
10. Sales cycle optimization (Focuses on streamlining the sales process)
This KRA emphasizes reducing the time it takes to close a deal by improving lead qualification and communication strategies.
Example: Reduce the average sales cycle by 5 days through improved lead qualification and implementing a system for faster follow-up with leads.
Success metric: Track the average time it takes to close a deal and analyze the effectiveness of implemented changes.
11. Team building (Strengthens collaboration and communication within the team)
This KRA focuses on fostering a collaborative and supportive team environment where members work together towards shared goals.
Example: Organize two team-building activities per quarter to encourage collaboration and communication, such as brainstorming sessions or social events.
Success metric: Conduct surveys to measure team cohesion and communication. Track the number of successful collaborative projects completed by the team.
12. Territory management (Ensures effective allocation of resources and workload)
This KRA emphasizes the sales manager’s ability to strategically assign territories and accounts to team members based on their skills and experience.
Example: Analyze customer data and workload to optimize territory allocation, ensuring each team member has an achievable quota and access to qualified leads.
Success metric: Track quota attainment for individual team members based on their assigned territories. Analyze the win rate for deals within each territory.
13. Sales forecasting accuracy (Improves planning and resource allocation)
This KRA focuses on the sales manager’s ability to develop accurate sales forecasts to guide resource allocation and decision-making.
Example: Implement a sales forecasting process that considers historical data, market trends, and individual sales pipelines. Achieve a forecasting accuracy of +/- 10% compared to actual sales results.
Success metric: Track the variance between forecasted and actual sales figures over time. Analyze the reasons for discrepancies and refine the forecasting process for improved accuracy.
“While forecasting sales, a cookie-cutter template can’t work for every business. Successful businesses aim to balance the top-down and bottom-up approaches so that the outcomes of both the forecasts align at a common ground. It proves to be a great way to ensure that your sales targets help your business grow, at a realistic rate.”
– Aiwin Joshy, Associate Director- Finance and Accounts, LeadSquared
14. Competitive analysis (Provides insights to gain a market edge)
This KRA emphasizes the sales manager’s ability to gather and analyze competitive intelligence to develop effective sales strategies.
Example: Conduct regular competitor analysis to understand their strengths, weaknesses, and pricing strategies. Use this information to tailor sales pitches and identify potential customer needs not met by competitors.
Success metric: Track the number of deals won against specific competitors. Analyze the win/loss ratio and identify areas where competitive intelligence can be leveraged more effectively.
15. Sales process adherence (Ensures consistency and quality in customer interactions)
This KRA focuses on the sales manager’s ability to ensure the team follows established processes, leading to consistent and effective customer interactions.
Example: Develop and implement a clear process that outlines each stage of the sales cycle and key communication points. Monitor adherence through call recordings and customer feedback.
Success Metric: Track the win rate for deals where the process was strictly followed compared to those with deviations. Analyze customer feedback for mentions of positive sales interactions.
A Sample KRAs Sheet for Sales Manager You Can Upload in DarwinBox or Any HRMS Tool
Here’s a sample KRA sheet of a sales manager.
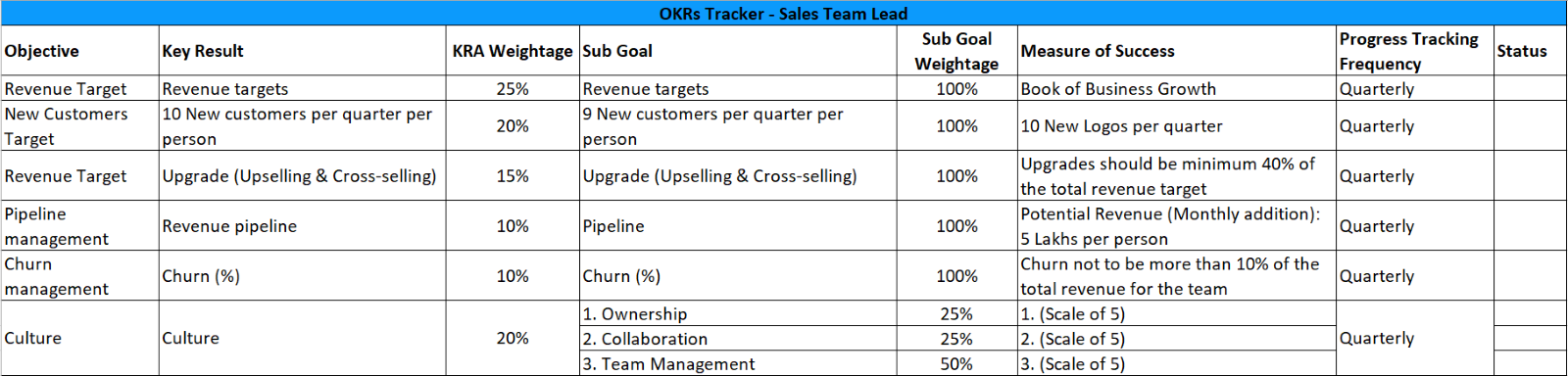
Click here to download this sheet
Tracking Your Sales Manager’s Performance Basis Defined KRA
Here are some methods you can use to track the performance of a sales manager:
1. Metrics & data tracking
- Sales KPIs: Monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) relevant to your sales goals. These can include revenue generated by the team, quota attainment, lead conversion rate, sales cycle length, and customer retention rate.
- Activity metrics: Track sales activity metrics such as the number of calls made, emails sent, presentations delivered, and proposals submitted. While activity doesn’t directly translate to sales, it can indicate effort and identify areas for improvement.
- CRM software: Utilize a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software to centralize data on leads, opportunities, and customer interactions. This allows you to monitor individual and team performance, identify trends, and measure progress towards goals.
If you’re stuck managing leads in a spreadsheet maze? Our CRM software automates tasks, tracks deals, and boosts your sales pipeline.
2. Performance reviews & feedback
- Regular reviews: Conduct regular performance reviews with your sales managers. Discuss their progress against KRAs, identify areas for improvement, and provide constructive feedback.
- Coaching & development: Implement a coaching and development program to help sales managers refine their skills and knowledge. This can involve one-on-one sessions, training workshops, or mentorship opportunities.
3. Customer feedback
- Satisfaction surveys: Gather feedback from customers about their interactions with the sales team. This can reveal insights into the effectiveness of communication, product knowledge, and overall customer experience.
- Win/Loss analysis: Analyze the reasons behind won and lost deals. This can identify strengths and weaknesses in the sales process or highlight areas where the sales manager can provide better support to their team.
4. Additional considerations
- Teamwork & collaboration: Evaluate the manager’s ability to foster a collaborative work environment. Observe communication dynamics, collaboration on deals, and overall team morale.
- Problem-solving & adaptability: Assess the manager’s ability to identify and solve problems, adapt to changing market conditions, and implement new strategies as needed.
- Long-term growth: Track the manager’s contribution to developing the skills and knowledge of their team members, which is crucial for long-term success.
By combining these methods, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of a sales manager’s performance and identify areas where they can excel. Remember, effective performance tracking should be a two-way street, providing valuable insights for both the manager and the organization.
FAQs
1. How can a sales manager effectively measure their performance against KRAs?
To measure performance against KRAs, you can track metrics like sales revenue, conversion rates, customer satisfaction scores, and team productivity. Regularly tracking these metrics in your CRM will provide insights into strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
2. What strategies can a sales manager adopt to achieve their KRAs?
Sales managers can adopt the following strategies to achieve their KRAs.
1. Setting clear goals and targets
2. Providing ongoing training and development opportunities for the team
3. Implementing effective sales processes
4. Fostering a culture of teamwork and collaboration









