Merchant onboarding- the often overlooked, yet crucial, process in the world of business. It’s more than paperwork; it’s the gateway where businesses and payment platforms align for seamless transactions.
In this blog, we dive into the practical strategies and insights that define successful merchant onboarding, shedding light on its pivotal role in forging strong business partnerships.
What Is Merchant Onboarding?
Merchant onboarding involves enrolling and verifying businesses, and providing them with the tools needed to accept payments. It’s an essential process that equips merchants with the infrastructure for accepting payments, often in e-commerce or retail settings.
It involves tasks such as identity verification, compliance checks, setting up payment systems, and ensuring adherence to security standards.
The goal is also to streamline and expedite the entry of new merchants into a payment network or platform.
The Purpose and Importance of Merchant Onboarding

Merchant onboarding is like the backend manager of business transactions. Its main job is to help businesses get ready to accept customer payments securely.
Did you know, on an average, 28.4 crore digital transactions are made daily in India?
Considering such a heavy number, any kind of fraud in this process can cost businesses billions. But here’s the catch: an efficient merchant onboarding process can reduce fraud rates.
Hence, the importance of merchant onboarding resonates in its impact:
1. Trustworthiness and security
By meticulously verifying merchants, authenticating identities, and implementing stringent compliance checks, this process safeguards against fraudulent activities. It protects both businesses and consumers from potential risks.
2. Operational fluidity
Imagine the issues businesses face while trying to set up shops without the necessary tools or understanding of payment systems. Merchant onboarding minimizes these obstacles, providing a seamless pathway for businesses to start selling, ensuring they comply with regulations.
3. Customer confidence
When businesses undergo a rigorous onboarding process, it indirectly assures customers of a commitment to security and reliability, elevating consumer trust in the brand and the overall transaction experience.
Now that we’ve understood what merchant onboarding is and why it is important, let’s read more about the steps which are involved in the process.
Steps in the Merchant Onboarding Process
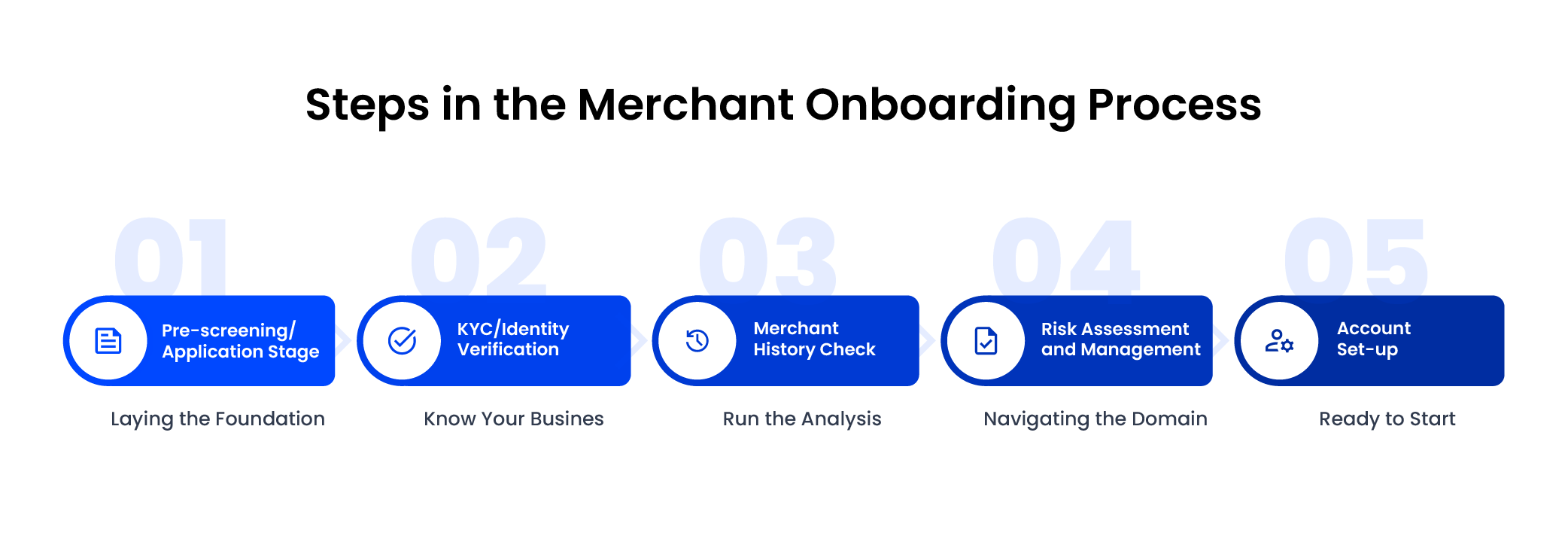
1. Pre-screening
Picture this as the first step in opening up a digital shop.
Businesses submit their applications, initiating the onboarding process. This stage involves preliminary checks to evaluate the business’s suitability for onboarding.
Why is this crucial?
A thorough pre-screening checks out potential issues, ensuring a smoother path ahead.
2. KYC or identity certification
Ever wondered how businesses prove their credibility in the digital space?
It happens through KYC verification—Know Your Customer, or in this case, Know Your Business.
This step verifies the identity of the business or merchant. It involves validating essential details, such as legal documentation, ownership, and authenticity.
Nearly 58% of fraud cases are associated with incorrect identity verification. KYC serves as the shield, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring trust between businesses and payment platforms. Merchant identity assessment plays a crucial role in the KYC process by adding necessary checks to enhance fraud detection and ensure the legitimacy of new merchant accounts.
3. Merchant history check
In this process, a thorough history check is conducted by the PSP (Payment Service Provider) to assess the merchant’s past business practices, financial history, and any potential risks.
This involves scrutinizing previous merchant accounts, verifying business legitimacy, and evaluating any history of fraud or chargebacks. The purpose is to ensure the new merchant aligns with ethical standards, complies with regulations, and poses minimal risk to the payment system or customers.
4. Risk assessment and management
Here, an analysis of potential risks associated with onboarding the merchant is conducted through merchant risk management. Factors like the business model, industry, and transaction volumes are assessed to manage and mitigate risks effectively.
From industry-specific threats to transaction vulnerabilities, this step evaluates it all.
Shockingly, around 70% of businesses experience fraud at least once. Hence, this critical assessment is necessary to ensure a safer environment for transactions.
5. Account set-up
Once the merchant is verified and approved, an account is created with the PSP or payment gateway. For seamless payment processing, this requires linking the merchant’s mobile app, POS system, or online store to the PSP’s payment gateway. Payment gateway technical assistance may be needed for the integration, in addition to testing to make sure everything functions as it should.
Now that we’ve understood the preliminary stage of merchant onboarding, let’s explore a field that transformed the merchant onboarding process – digital transformation.
Digital Transformation in Merchant Onboarding
The landscape of merchant onboarding evolves hand in hand with technological advancements.
The digital advancement has revamped the conventional method of merchant onboarding. The steps are now characterized by enhanced efficiency, speed, and bolstered security measures.
Let’s understand more about this process.
1. Automated business verification
Gone are the days of manual checks and prolonged waits.
With digitization, businesses now undergo a swift and automated verification process.
This accelerated method expedites the onboarding journey.
Industry statistics highlight that businesses experience a 50% decrease in onboarding time with automated verification processes, allowing them to dive into the market quicker and more efficiently.
2. Identity verification
Verifying identities has undergone a digital facelift.
The advent of AI-driven technologies and machine learning algorithms ensures that Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are not just stringent but swift.
For example, this digital transformation has led to a 40% reduction in identity-related fraud cases for Driveway, a subsidiary of Lithia Motors, enhancing security while ensuring a seamless onboarding experience for businesses.
One prominent AI technology that has revolutionized the KYC (Know Your Customer) process is Optical Character Recognition (OCR). OCR technology enables automated data extraction from various identity documents, such as passports, driver’s licenses, or IDs. It swiftly digitizes and interprets the information, expediting the identity verification process.
However, with the evident digital transformation in place, the need to delve deeper into the critical aspects of compliance and fraud prevention in merchant onboarding has become prominent.
Let’s discuss it a bit.
Compliance and Fraud Prevention in Merchant Onboarding
Understanding compliance and fraud prevention in merchant onboarding is crucial for ensuring secure transactions, bolstering trust, and safeguarding businesses and customers against financial risks.
Legal compliance factors are essential standards that merchants must adhere to during the onboarding process, especially in high-risk industries like gaming and foreign exchange.
1. Compliance measures during onboarding
Compliance measures play a pivotal role in ensuring businesses adhere to regulatory standards. AI-driven systems streamline the adherence process, ensuring compliance with evolving Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. These systems, equipped with advanced algorithms, ensure swift verifications while staying aligned with the ever-changing compliance landscape.
Let’s learn some more about these systems:
KYC (Know Your Customer) verification
KYC verifies customer identities, ensuring businesses understand who they are dealing with. Advanced AI-powered KYC tools swiftly authenticate IDs, reducing onboarding time, enhancing security, and aligning with evolving regulatory requirements to prevent fraud.
For example: Jumio is a leading provider of AI-powered identity verification and KYC solutions. Their AI-driven software assists businesses in verifying customer identities remotely in real-time, ensuring compliance with regulations while minimizing fraud risk.
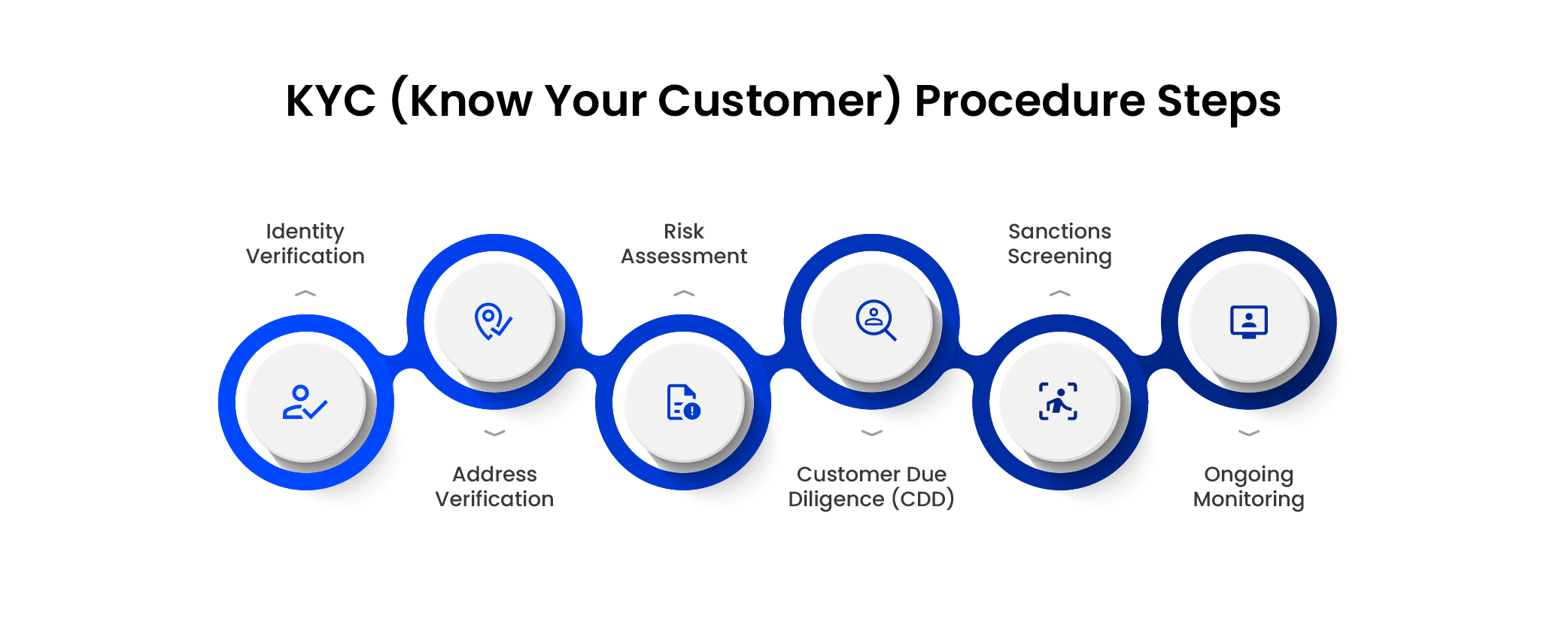
The KYC (Know Your Customer) procedure involves several steps:
- Identity verification
Collect official documents (ID cards, passports) to confirm the customer’s identity.
- Address verification
Validate the customer’s residential address through utility bills, bank statements, or government-issued documents.
- Risk assessment
Analyze the customer’s profile and transaction history to assess any potential risk or suspicious activities.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Conduct in-depth checks on the customer’s background, including business relationships and source of funds, for higher-risk accounts.
- Sanctions screening
Screen customers against global sanctions lists and databases to ensure they’re not involved in illegal activities or on watchlists.
- Ongoing monitoring
Continuously monitor customer transactions and behavior to detect any anomalies or changes that may indicate risk.
AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
AML measures aim to detect and prevent money laundering activities. These days AI-driven AML tools analyze transactional patterns, flagging suspicious behavior to prevent illicit financial activities, ensuring businesses comply with legal regulations and mitigate financial risks.
For example: Onfido is another prominent provider of AI-powered identity verification solutions. Their platform combines AI, machine learning, and facial recognition technology to verify identities by analyzing government-issued IDs and biometric data.
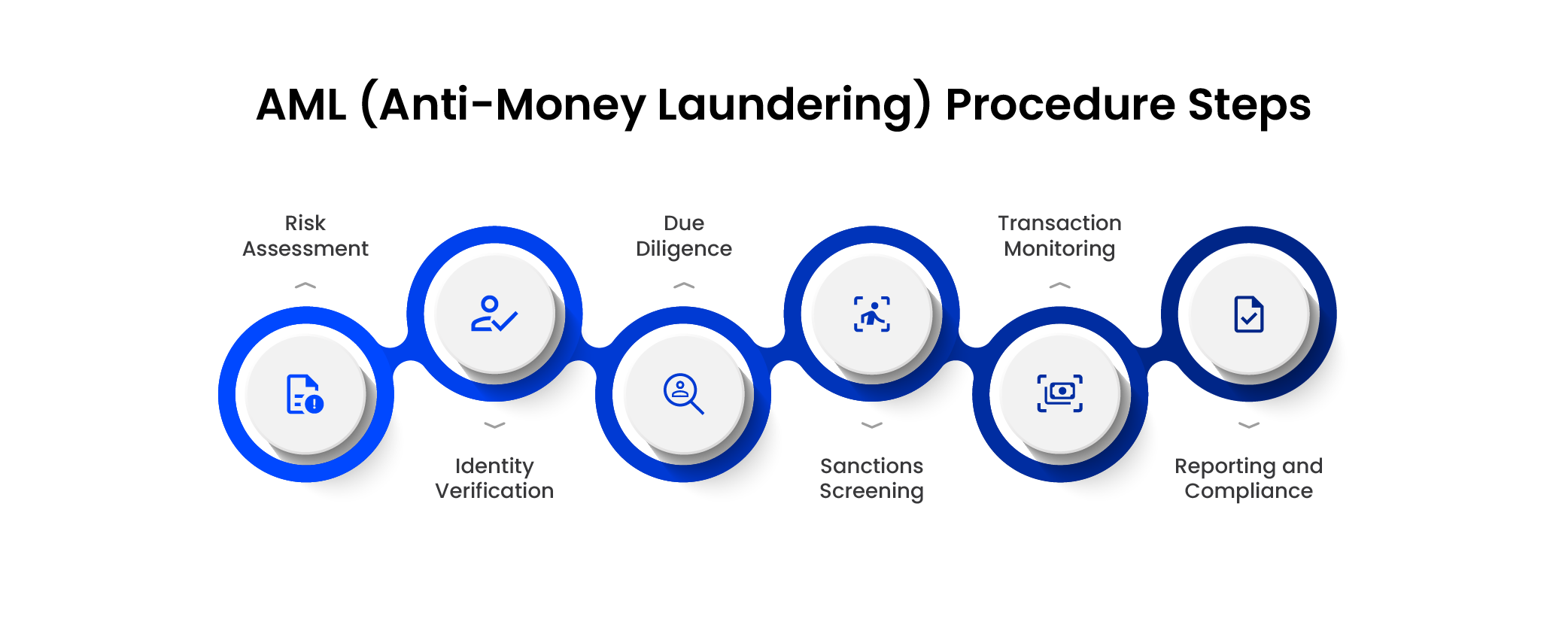
The Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedure during merchant onboarding involves specific steps:
- Risk Assessment
Evaluate the risk associated with onboarding a merchant based on their industry, geographic location, business type, and clientele.
- Identity Verification
Verify the merchant’s identity through official documents, ensuring they match the provided information.
- Due Diligence
Conduct thorough due diligence to understand the merchant’s business model, ownership structure, financial transactions, and expected volume.
- Sanctions Screening
Screen the merchant against global sanctions lists to ensure they are not involved in illegal activities or associated with sanctioned entities.
- Transaction Monitoring
Implement systems for ongoing monitoring of the merchant’s transactions to detect any unusual patterns or suspicious activities.
- Reporting and Compliance
Ensure compliance with AML regulations by documenting and reporting any suspicious activities to relevant authorities while maintaining records as required.

Fraud poses a significant threat to businesses venturing into digital transactions.
However, AI-powered fraud prevention tools act as vigilant guardians, continuously monitoring transaction patterns and user behavior in real time.
This proactive approach leads to a substantial decrease in fraudulent attempts. Risk management is an ongoing process that begins with merchant onboarding and must be maintained throughout the merchant’s lifecycle to prevent fraud. Let’s have a look at what process this approach entails and understand them through some examples.
Fraud detection systems
These systems employ machine learning algorithms to analyze transactional patterns, flagging anomalies or suspicious activities in real time. They proactively identify potential fraudulent transactions, mitigating risks before they impact the business.
Example: Citibank utilizes AI-driven fraud detection systems to analyze transactional patterns. By employing machine learning algorithms, they swiftly flag suspicious activities in real time, preventing potential fraudulent transactions. These systems proactively identify anomalies, mitigating risks and safeguarding customers’ financial assets.
Behavioral analytics
AI-driven behavioral analytics assess user actions and patterns, establishing a baseline of normal behavior. Any deviations from this baseline trigger alerts, helping prevent unauthorized access or fraudulent transactions.
Example: Facebook leverages AI-driven behavioral analytics to protect user accounts. By establishing a baseline of normal user behavior, any deviations trigger immediate alerts. Unusual login locations or atypical patterns of engagement prompt security measures, preventing unauthorized access and ensuring user data security.
Predictive analytics
Leveraging historical data, predictive analytics forecast potential fraud risks. Machine learning models analyze patterns to predict and prevent fraudulent activities, enhancing security measures during onboarding.
Example: Anthem, a health insurance provider, employs predictive analytics using AI to detect fraudulent claims. By analyzing historical claims data, their machine learning models predict potentially fraudulent activities. This proactive approach helps Anthem anticipate and prevent fraudulent claims, saving costs and maintaining the integrity of their insurance services.
Integrating these AI-powered tools increases the security of merchant onboarding, effectively mitigating fraud risks and ensuring a safer environment for businesses and consumers alike.
Merchant Support and Continual Relationship Building
Supporting merchants extends beyond onboarding merchants; it’s an ongoing relationship.
Providing comprehensive assistance post-onboarding ensures merchants thrive. Regular check-ins, troubleshooting aids, and guidance on optimizing their services foster strong, lasting relationships.
Post-onboarding support for merchants
- Prompt addressing of concerns
Timely resolution of merchant queries or issues after onboarding ensures seamless operations and a better experience. - Resource provision for growth
Offering access to tools, educational materials, or growth-oriented resources aids merchants in expanding their businesses. - Facilitation of training sessions
Conducting sessions or workshops post-onboarding equips merchants with essential skills and knowledge, fostering their success. - Consistent communication
Regular communication provides transparency, keeps merchants informed, and strengthens relationships. - Transparency in operations
Being open and transparent in deals builds credibility and trust in business partnerships. - Proactive problem-solving Addressing issues before they escalate demonstrates a commitment to mutual success and reliability.
Now that we’ve understood the nuances of merchant onboarding, let us also have a look at how LeadSquared can be of use here.
Merchant Onboarding with LeadSquared
Merchant Onboarding with LeadSquared

Merchant Onboarding with LeadSquared provides a unified platform that seamlessly combines streamlined efficiency, automated processes, and insightful analytics, facilitating collaboration with payment service providers. This comprehensive solution ensures a swift and seamless journey, leading the merchants towards sustained success.
Let’s have a look at some of its features:
1. Fast onboarding LeadSquared ensures a swift entry for new merchants with zero delays. Automating merchant-agent mapping and enabling one-click additions expedite the process, ensuring businesses get up and running swiftly.
2. Self-serve portals Empowering merchants with self-serve portals improves listing rates. The direct drop-off to call centers ensures instant support, enhancing the merchant’s experience and speeding up resolutions.
3. Paperless verification Say goodbye to paperwork hassles. With LeadSquared, documents are digitally uploaded for verification, with instant approval or rejection, streamlining the verification process effortlessly.
4. Field agent productivity LeadSquared optimizes field agent productivity with the help of field force tracking system by planning their day effectively. Agents easily identify nearby vendors, track their activities, and ensure a seamless onboarding experience.
5. Merchant engagement Engage merchants proactively with LeadSquared’s relevant insights. Empower them to learn and grow by providing valuable insights tailored to their needs and business goals.
6. In-depth insights Gain comprehensive insights into vendor onboarding, team performance and vendor analytics. These insights help refine strategies and provide merchants with the necessary tools to enhance their performance.
7. Getting started With LeadSquared, kickstarting your merchant onboarding journey is simple. Explore the platform’s intuitive interface, automated processes, and data-driven insights. Maximize efficiency, engagement, and success in your merchant onboarding endeavors.
Discover How LeadSquared Revolutionized Amazon Pay’s Merchant Onboarding Process
LeadSquared streamlines merchant onboarding with its efficient tools and insightful analytics, ensuring a smooth and productive journey for businesses and merchants alike.
Amazon Pay, a leader in digital payment services, streamlined their merchant onboarding operations using LeadSquared.
They loved LeadSquared because it helped:
- Streamline merchant onboarding
- Bring structure to the process
- Improve process and agent efficiency
- Create more visibility in the business process
Read more, here.
In Conclusion
Merchant onboarding serves as the coordinator between secure transactions and a smooth entry for businesses into the digital realm.
Its importance lies in bolstering trust, security, and operational fluidity, safeguarding both businesses and consumers.
With LeadSquared offering streamlined efficiency and insightful analytics, businesses can embark on a swift, secure journey to success in merchant onboarding.
To know more, get in touch with us by booking a demo.
FAQs
Merchant onboarding includes steps like application submission, identity verification, compliance checks, and setting up payment systems. It ensures businesses are equipped to accept payments securely.
KYC (Know Your Customer) verifies merchant identities, validating essential details to prevent fraud. It ensures authenticity, safeguarding businesses and customers in transactions.
The duration varies based on factors like industry, verification complexities, and compliance requirements. Typically, it can take a few days to several weeks for completion. ral weeks for completion.









