In this article, we will explore the market opportunities amidst the changing retail lending landscape and how lenders can differentiate themselves from the competition.
Retail lending is the process of disbursing any form of loan to an individual customer. The retail lenders generally include banks, credit unions, savings u0026 loan institutions. However, today, Fintechs are also providing credit options to borrowers. Apart from these, third-party lenders may partner with retail businesses to offer credit to customers.

Market Opportunity
Lending itself accelerates business activities and can boost the economy. A joint report by ICICI Bank and CRISIL in late 2019 predicted retail loan growth to reach 96 trillion INR in 2024. The overall technological progress, financial behavior, and consumer trends before the pandemic indicated a strong growth for the retail lending market. Data analytics tools and automated underwriting systems will make it much easier to disburse loans to consumers.
During the pandemic, the internet played a significant role in keeping people connected and businesses up and running. Consumers are now using digital payment more than before. The payment sector has already received both private funding and government assistance. Therefore, it is inevitable that other financial services, such as lending, will be digitized.
Today, new business models such as peer-to-peer (P2P) lending and Point-of-Sale (PoS) financing are emerging. Alternate data assessment methods allow consumers to get small personal loans, who previously would not get loans from a bank. It is also enabling millennials working as freelancers or gig economy workers to get loans.
India’s retail lending market was experiencing steady growth before the pandemic. However, the global economy crashed dramatically during the pandemic. India was one of the worst-hit countries. Private consumption in India fell to 21.7 trillion INR in the first quarter of 2020-2021 from 32.5 trillion INR in the first quarter of 2019-2020. The demand for retail loans was low, despite the RBI reducing the interest rates.
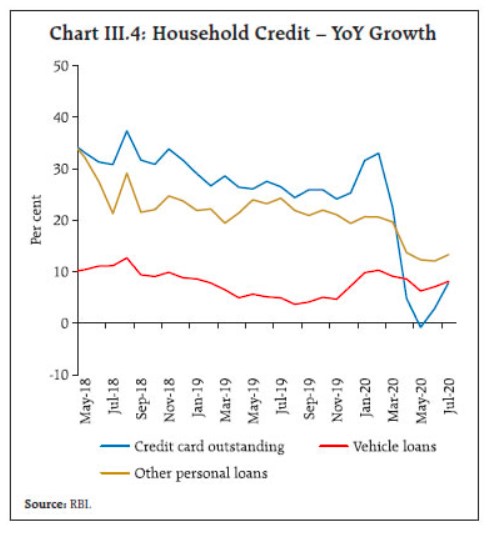
The pandemic changed how banks and other financial institutions operate. Now, with the pandemic gradually subsiding and the economy returning to normal, here are some of the key points that businesses and consumers need to keep in mind when dealing with retail loans.
The new retail lending landscape
One of the recent changes in the retail loan is doing away with face-to-face interactions. During the disbursement of loans, banks and financial institutions heavily relied on in-person interactions and paperwork. During the pandemic, such interactions were deemed unsafe, and businesses had to adopt digital methods overnight.
In India, banks heavily relied on in-person interactions when processing loans, right from the sourcing to the disbursal. This required changing.
Here is an example.
Edelweiss Retail Finance had to change its customer journey and align it more with paperless processes. Their entire loan application process became contactless. The KYC process used machine learning-based methods, video chats, and voice bots. The automation also helped the company to cut down its file processing costs.
Similarly, HDFC bank partnered with Adobe to personalize the digital journey of its retail customers. The artificial intelligence-driven processes enabled marketing, advertising, and personalization. The customers could now apply for loans at any time, from any device of their choice.
Watch the webinar: Transforming Lending: how to ensure a paperless and contactless lending process?
Change in consumer preferences:
The pandemic has also forced consumers to adopt digital means. While the younger generations inherently prefer online interactions, the older crowd still wants in-person interactions. The pandemic has pushed the digitization drives that a lot of banks started. As a result, existing customers are also open to digital banking. At present, a hybrid approach is a preferred choice for accommodating all forms of customers. Banks will offer high-value physical interactions only if necessary while keeping the core services digital.
The rise of fintechs:
The increased digitization has accelerated India’s growing fintech businesses. For instance, the digital lending app Navi recently received an investment of 239 million USD. Netherlands-based PayU acquired PaySense for 185 million USD. Medici reports that India’s 338 fintech startups will serve as alternate lending platforms because of technologies such as Unified Payments Interface (UPI), Aadhaar authentication, and eKYC. These technologies offer quick background checks and instant loans. It will particularly benefit the rural and the underserved population.
Fintechs can help in lending in multiple ways. These include:
- Marketplaces that connect borrowers with lenders
- Peer-to-peer lending
- Instant loans
- On-book lending provided by non-banking financial institutions
- Crowdfunding for microloans
IndiaStack has played a crucial role in the digitization of payments and lending. Furthermore, RBI eased regulations, allowing video-based customer identification processes. eKYC, eSign, and DigiLocker also provide the necessary and reliable security infrastructure needed to process loans.

Differentiator strategy for retail lenders
The Indian retail lending market has many fintech startups that offer retail lending services. Here are some of the key differentiating strategies that these companies use.
Point-of-Sale Financing
PoS Financing is a personal loan that the customer obtains as they pay for something they want to buy. The purchase can be furniture, electronics, or even groceries. The business provides a loan to the customer, given that they purchase a product from the store. It is like buying an item using a credit card where the customer pays the bill later. However, in this case, the business knows the exact reason for the loan. Moreover, there is no application process, and customers can get them instantly. Also, these loans often have no interest associated with them.
PoS financing allows businesses to increase their customer base. Traditional loans are provided only to those customers who have a good credit score. However, PoS financing is for any consumer. Those who cannot pay the entire sum directly can pay in monthly installments. PoS financing also increases sales without credit risks. PoS financing has become popular since millennials are averse to having loans or credit cards. This form of lending allows consumers to borrow small amounts instantaneously without any paperwork. A popular PoS financing product in India is Amazon Pay Later.
Acquiring customers through an organization
Since the last decade, the gig economy has boomed in India. With the rise of platforms like Uber, Zomato, Swiggy, and so on, many people have opted for daily/contractual jobs. Delivery, eCommerce and logistics, and mobility segments created thousands of jobs. Opportunities for freelancing jobs have also increased. The younger generation is more inclined towards freelancing jobs as artists, designers, writers, software developers, and more as these jobs provide more flexibility. However, the current banking system cannot accommodate such consumers when it comes to retail loans.
Traditional retail loans look for stable income sources. Fintech companies are now targeting freelancers and gig workers via organizations that digitize such segments. For example, the Bengaluru-based company Goddard Technical has rolled out a program called Avail Assist. The program provides loans to the contract workforce. They also offer insurance for blue-collar workers and short-term loans to the financially underserved.
Digital lending marketplace
The marketplace model or the peer-to-peer (P2P) model allows borrowers and lenders to connect using an online platform. It is one of the most flexible methods of getting loans. The platform aggregates borrowers and lenders and maps them accordingly. The platform is also responsible for verifying the authenticity of the borrowers and disclosing them to potential lenders. The advantage is that lenders can set interest higher than bank saving rates while borrowers can get a loan at a rate lower than that of the bank.
In India, RBI regulates P2P lending and has capped the maximum amount of loans across all platforms. At any point, a P2P lender can lend all borrowers a maximum of ₹50 lakh.
Direct customer acquisition
Startups can also provide small-ticket loans to consumers directly and help them build up a credit score. The more they take loans and repay on time, the better their credit score gets. A higher credit score will also enable the consumer to take larger loans in the future.
Companies are also using technology like Lending CRM software to streamline their customer acquisition process. Using such digital tools, they can achieve higher operational efficiency and manage interactions with the borrowers across their lifecycle.
The Bottom Line
Both banking institutions, as well as consumers, are adopting digitization methods. Even though the pandemic has caused an economic crisis, it has also given the digitization drives a much-needed push. Moreover, the digitization drives have enabled more people to participate in the retail lending sector, which was not possible previously.
Fintech startups have enabled underserved consumers to get loans during lockdowns. Financial institutions have now sped up loan application processes, incorporated automation, and cut down on back-office operational costs. In the post-Covid period, fintech startups have a window of opportunity as the urban population is open to adopting documentation-free lending services.
If you are looking for a digital lending solution to manage your process and teams – sales, call center, field sales, collections, and more, do check out LeadSquared Lending CRM.








