Alternative lending refers to the wide range of loan options available to consumers and business owners outside of a traditional bank loan. In other words, it is the process of receiving loans from non-banking institutions or other financial institutions that have not received a full banking license. Alternative lending has grown drastically over the last few years as traditional banks have failed to provide financing to blue-collar workers, freelancers, or gig workers because of their incomplete credit history.
In developing countries, a large section of the population still rely on primitive methods to get loans. People often go to pawn shops, deposit their valuables, and get loans. In other cases, people take loans from friends and family.

Alternative lending, also known as alt lending, received a boost during the pandemic as small and medium-sized businesses were gravely affected globally. Many companies had to shut down because of the lockdown. Numerous smaller companies went bankrupt, and many business owners did not have the capital to restart their business once the lockdown lifted. Often, these small business owners did not have the credit history to get a loan, while those with a record of bankruptcy would find it challenging to get any financing from a traditional bank.
Amidst this, non-banking institutions are swiftly filling in the gap by serving the subprime unbanked group of customers. Alternative lenders make use of technology to penetrate a market that was unexplored by the traditional banking systems. Moreover, they are making a higher profit by providing a large number of smaller loans. In fact, 40% of retail customers think that a non-bank will offer better investment services, according to a survey by Oracle.
Let us dive into the industry trends, market opportunities, and emerging business models in the alternative lending sector.
The rise of technology-driven alternative lenders
The fintech space, over the last few years, has enabled companies to turn data into profits. Fintech companies have disrupted the long-standing banks by focusing on technological innovations to understand risk better. Fintech innovations allowed improved data collection. This data helped in streamlining the underwriting process. Furthermore, advancements in AI allowed underwriters to make decisions faster. All this together provided faster loan disbursement and greater customer satisfaction.
Alternative lenders have a clear advantage over banks when it comes to approval ratings. They can assess a higher number of factors that determine the creditworthiness of an applicant. Whereas banks only look at the financial statements and previous loan repayment records. However, that data is often not a good indicator of one’s financial health.
The differentiator:
Alternative lenders use a combination of computer algorithms, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to mine the applicant’s data. This data often includes personal finances, spending habits, purchase records, and more. The applicant may also need to show their rent payment records, utility bills, telephone bills, and more. Some digital lending platforms also use social media data to understand the financial health of the applicant. With this data, they also gauge their ability to pay back the loan. These data points, taken together, can often show that an applicant has good financial health despite having a thin credit profile. However, in the entire process, the data collection is done with the consent of the applicant. The applicant must agree to share their data to get the loan.
There is one more reason why MSMEs favor alternative lenders. Not only can they provide loans to subprime applicants, but they also provide a better experience than any traditional bank. The fast adoption of digital lending platforms has made the loan application process effortless. The borrower can quickly upload the required documents and receive instant pre-approval letters. The lending decision takes place in a matter of days.
Traditional banks have also been active in this space and have been integrating state-of-the-art processes into their banking operations. Banks have introduced electronic payment and online services for a while now. Many banks have partnered with fintech services to provide a better customer experience. However, banks deliver a different set of financial services than non-banks and alternative lenders. They must abide by government regulatory policies and cannot be as flexible as fintech companies.
Types of alternative lenders and alt lending market size
The most popular forms of alternative financing available are:
- Credit Unions
- Community Development Financial Institutions (CDFI)
- Microlenders
- P2P (Peer-to-peer) Lenders
- Crowdfunding
- FinTechs
- Marketplace lending
Alternative lending market size, United States
- Total transaction value in the Alternative Lending segment is projected to reach US$8,684.9m in 2022, with marketplace lending being the largest market segment.
- The alternative lending sector is expected to show an annual growth rate of 2.4% (CAGR 2021-2025).
- (Source: Statista)
Alternative lending market size, Worldwide
- Total transaction value in the Alternative Lending segment is projected to reach USD 334,277.7 million in 2021, with crowdlending being the largest market segment globally (USD 241,582.2 million).
- The sector is expected to show an annual growth rate of 4.70% (CAGR 2021-2025).
- (Source: Statista)
Difference between banks and alternative lenders
Business models
Alt lenders have introduced multiple new types of lending such as non-bank lending, peer-to-peer lending, and small business alternative loans. They also offer services to small and medium-sized businesses, such as invoice factoring or equipment financing. With data analysis and automation, alternative lenders can predict risks more accurately, and they can approve loans to business owners instantly.
For example, Finnable, one of the fastest-growing fintech start-ups in India, promises to grant loans in less than 1 minute. However, processing a loan involves document collection, background verification, underwriting, and loan disbursal. If done manually, it can take several days. To overcome this challenge, they actively use workflow automation in their Lending CRM. In the system itself, the borrower can upload KYC details, and the details are automatically passed on to the credit/underwriting team for verification and loan disbursal.
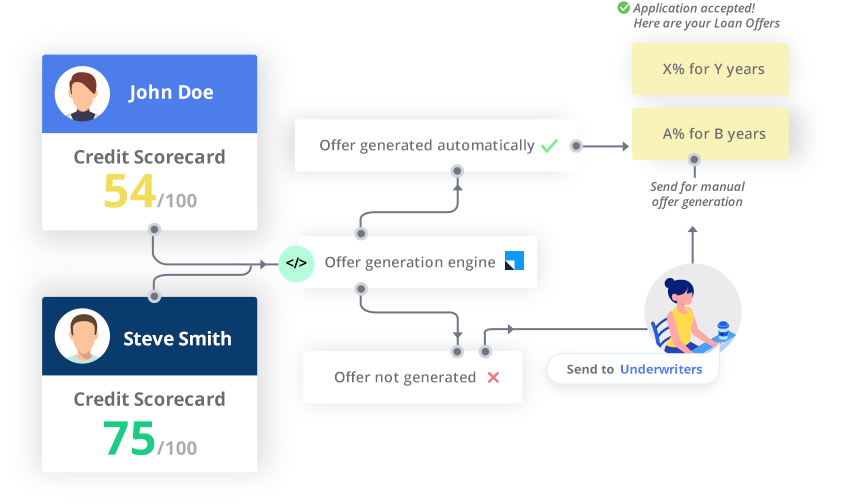
Banks employ a more traditional workflow where a loan application includes bank statements, investment accounts, tax return forms, and more. The application can take weeks to get approved. Small business owners may not have all these documents. Hence, traditional banks may be a less favorable endeavor altogether.
Interest rates and loan tenure
Alternative lenders charge a higher interest rate, ranging from 5 to 13%. However, since alternative lending takes place for short terms, the interest amount is often low. Banks provide loans for three to five years, where alternative lenders generally issue loans from 1 to 3 years. Also, alt lenders readily give small loan amounts for less than a year.
Application process
Alternative lending platforms offer an easily accessible application process. The entire process is digitized, and it often as simple as signing up for a website. Most of the tasks are automated, so neither the borrower nor the lender has to deal with any rigorous paperwork. These applications also have a much faster turnaround time.
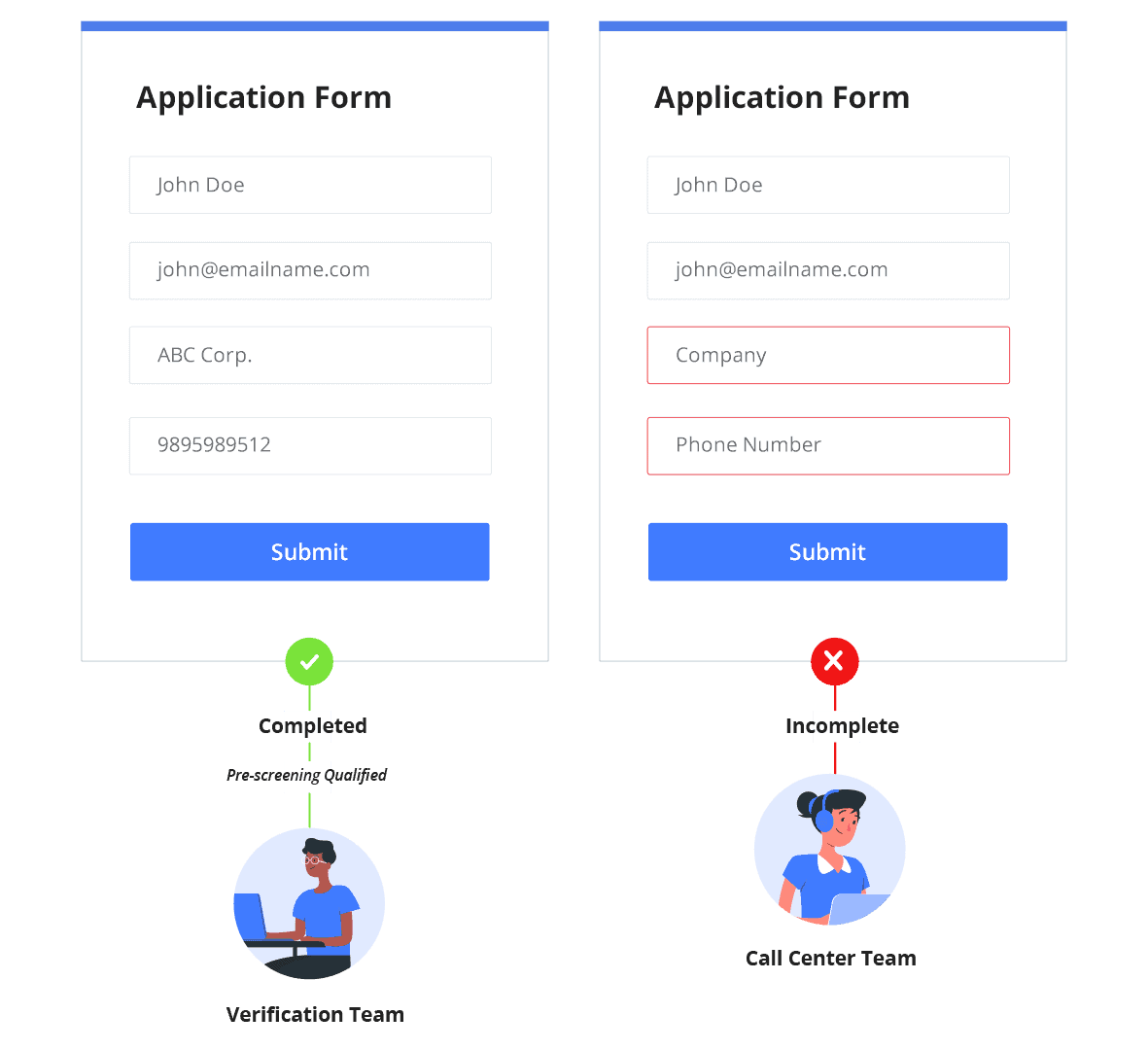
Traditional banks have their own established workflow where you may need to provide a hard copy of documents at the bank branch. The turnaround time is also much higher.
Notable trends in alternative lending industry
Alternative lending has matured in economies like the US, UK, and China, where firms have started early. In developing countries like India, regulators are looking forward to providing a sound legal framework. At this moment, this segment shows massive growth potential. It is because there is a shortage of cash supply, and this industry can address that. Also, the legal barriers for these firms are far fewer. Here are some of the distinctive trends.
1. Different working models for developed and developing economies
Developed economies largely depend on consumer financing. It includes payment of credit card dues, housing, or education loans, refinancing existing loans, or purchasing goods and services. In developing economies, the target of alt lending platforms is to reach out to unbanked businesses and individuals.
2. Alt lending platforms are a viable option for investment.
Alternative lending has emerged as a viable asset class. It is a less volatile option for investors, both retail and institutional. These investments are less complex and provide decent returns for the short term. Hedge funds, investment banks, and insurance companies have already invested a lot in alternate lending.
3. Restructuring of traditional banks
Banks all over the world are closely observing this space and are starting to get involved. Since banks cannot entirely change overnight due to regulations, they are incorporating some features of alternate lending into their operations. Banks are now streamlining the loan application processes. Some banks have partnered with alternative lending firms to provide their financial services with the bank’s branding.
4. Transparency has become crucial.
Alternative lending is addressing the gap left by the 2008 financial crisis. The recent pandemic showed the lack of capital for smaller enterprises. Since then, there was a steady push for transparency in the banking sector. Still, bank frauds took place anyways. Now, with stricter regulations, banks do not have the flexibility that these alternative lenders have. Therefore, alternative lending firms must build trust and be transparent about their pricing. This way, they can avoid getting their hands tied by excess regulations.
5. A secondary market for online credit
Even though it is at a nascent stage, online lenders are now trying to bundle small-ticket loans and sell them to other institutional lenders. This emerging market model allows lenders to spread out the risk and secure additional sources of funding.
The bottom line
In countries like the US, private SMBs employ 60% of the workforce. Due to the cash crunch and the lack of support from incumbent banks, alternative lending is a massive threat to traditional banks. Even though the lending business has been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, alternative lenders have continued to help investors and borrowers. However, there still exists some challenges. The uncertainty in the regulatory framework is thwarting the growth of this segment. There is also a lack of technology players for this space. Implementing advanced analytics and data mining tools can therefore be expensive for these firms. Identifying the target customer and building trust is also a time-consuming affair.
With the rise of fintech firms and digital lending platforms, alternative lending is here to stay. When it comes to business lending, traditional banks still have the majority market share, but their growth has plateaued. It has now become simpler for non-banking firms to digitize their lending process. Using dedicated tools such as CRMs, they can easily manage borrowers, customer onboarding, loan disbursal, collections, and more.
Read further:








