- Home
- Learn
- Healthcare
- A 9 Rule HIPAA Compliance Checklist to Guide You in 2026
HEALTHCARE
A 9 Rule HIPAA Compliance Checklist to Guide You in 2026
Contents
This guide is for healthcare providers — doctors, nurses, dentists, and anyone responsible for handling patient data. If HIPAA compliance is part of your job, this checklist will help keep you on track.
A terms and conditions box you could tick off and never look back again…
If that’s all it took to be HIPAA compliant, things would’ve been easier for healthcare providers.
But HIPAA doesn’t work that way. It’s not a set-it-and-forget-it deal; but an ongoing process that evolves with your practice.
Whether you’re just starting out or double-checking that everything’s in order, a HIPAA compliance checklist helps keep you on track.
This guide breaks down the key areas you need to review to make sure your practice stays HIPAA compliant — today, tomorrow, and beyond.

From medical history to appointment reminders, every exchange of sensitive patient info in healthcare comes with an expectation – that they remain private and secure.
HIPAA is a set of rules issued by the U.S government that makes sure that this expectation isn’t just a “good practice”, but the law.
Further Reading: What is HIPAA Compliance
So, who needs to comply with HIPAA?
Hospitals and healthcare practices would be the obvious answers. Under HIPAA, they are referred to as covered entities and are directly bound by its regulations. But it doesn’t stop there. Any business handling protected health information (PHI) — from insurance companies to billing services to healthcare CRM providers — must all be HIPAA compliant. They are the business associates with which covered entities like hospitals come into a pact – so that they can use their services while ensuring HIPAA compliance.
HIPAA entails strict rules around privacy, security, and what to do in case of a breach. Let’s do a quick rundown of some of its key rules for handling sensitive healthcare data.
Defines what qualifies as Protected Health Information (PHI) and sets strict guidelines on who can access, use, and share it. It also gives patients rights over their data, including access to records and request for corrections.
Focuses on protecting electronic PHI (ePHI) with administrative, physical, and technical safeguards. This includes access controls, encryption, and secure authentication measures.
Requires covered entities to notify affected individuals, the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS), and sometimes the media in case of a data breach.
Establishes penalties for non-compliance, including hefty fines and potential criminal charges. It also gives HHS the authority to investigate violations and conduct audits.
Penalties levied for violations of HIPAA compliance can be devastating depending on the severity or scale of the violation. And so they are tiered as seen below:
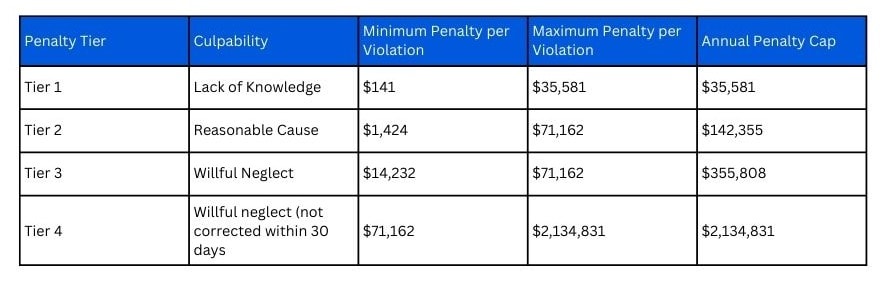
Extends HIPAA compliance requirements to business associates, ensuring third-party vendors handling PHI are equally responsible for data protection.
Together, these rules create a strict but necessary framework for safeguarding patient privacy.
A practical way to make sure you’re covering all the rules and the right bases is by using a HIPAA compliance checklist.
Before you can protect patient information, you need to know what qualifies as Protected Health Information (PHI). It’s not always as obvious as a medical diagnosis or lab report. PHI covers any information that can link a patient to their health records — even something as simple as an email address or phone number tied to an appointment reminder.
Think of it this way: if the information could identify a patient directly or indirectly and is connected to their healthcare services, it’s PHI. This includes:
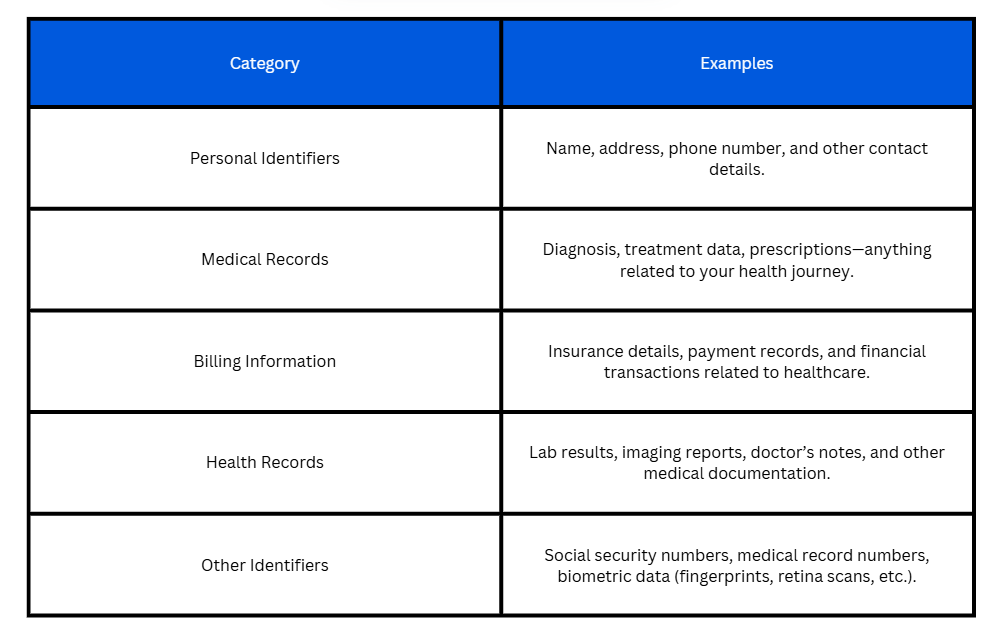
Whether you’re storing patient files, sending appointment confirmations, or sharing lab results with specialists—if the data links back to a patient, it needs to be protected. So, understanding what falls under PHI is the first step to building a solid HIPAA compliance strategy.

Not all risks are obvious. Take a hard look at how patient data flows through your organization. Where is PHI stored? Who has access to it? How is it transmitted? Are there weak spots that could expose sensitive information?
A thorough risk assessment helps you spot these gaps before they become breaches.

Many security breaches happen not because of sophisticated hacking but due to preventable vulnerabilities, such as:

HIPAA doesn’t set a fixed schedule, but industry best practices recommend:

Well-documented HIPAA policies are a must. These should outline everything from how patient data is stored and shared to what steps to take in case of a suspected breach. But policies alone aren’t enough—staff needs regular training to spot compliance risks in their day-to-day tasks.
A strong HIPAA training program should cover:

If a third-party vendor comes into contact with PHI on your behalf, their compliance is just as crucial as yours. Whether it’s a cloud storage provider, an email service handling appointment reminders, or a billing company processing patient payments, they must follow HIPAA regulations just like covered entities.
A Business Associate Agreement (BAA) is the safeguard that makes this official. It’s a legally binding contract that ensures vendors understand their role in protecting patient data and outlines the security measures they must uphold. Without it, your organization could be held responsible for any HIPAA violations they cause.
Before partnering with any service that interacts with PHI—be it an EHR system, a marketing platform, or an IT support team—make sure a signed BAA is in place.

Not everyone in a healthcare organization needs access to every piece of patient information. A front-desk receptionist scheduling appointments doesn’t need the same level of access as a physician reviewing lab results. That’s where access controls come in.
HIPAA requires that access to PHI be restricted based on job roles—a principle known as the “minimum necessary rule.” This means employees should only have access to the information they need to do their jobs, nothing more.
To enforce this, authentication measures must be in place. Strong passwords are a start, but they’re not enough. Multi-factor authentication (MFA)—like requiring a code sent to a phone or email—adds an extra layer of security. Role-based permissions ensure that sensitive data isn’t floating around where it shouldn’t be.

Healthcare runs on communication—emails confirming appointments, text messages reminding patients to take their medication, and digital records shared between providers. So, every message exchanged carries a risk if not properly secured.
To meet HIPAA standards, any electronic communication containing PHI must be safeguarded. That means using platforms with end-to-end encryption, ensuring messages can’t be intercepted or accessed by unauthorized parties. Standard email services and regular texting apps won’t cut it. Instead, healthcare providers should rely on HIPAA-compliant messaging platforms that offer encryption, access controls, and audit logs.
Beyond messaging, data transfers—whether uploading patient files to cloud storage or sharing lab results with a specialist—should also follow security protocols.
The bottom line? If patient information is being sent or received digitally, it must be locked down at every stage to ensure safety.
Further reading: HIPAA-Compliant Marketing

HIPAA compliance is an ongoing process. Regulations evolve, threats to patient data change, and healthcare organizations grow, bringing new risks into the equation.
Regular audits help identify gaps before they turn into violations. This means reviewing policies, assessing controls of access, checking security, and ensuring staff training is up to date. If anything falls short, updates should follow immediately—whether it’s refining internal protocols or upgrading security systems.
Staying compliant is also about building a culture where protecting patient information is second nature.

If it’s not documented, it didn’t happen. Healthcare organizations should adopt this mindset when it comes to HIPAA compliance. Audits, training sessions, risk assessments, and security incidents—everything should be recorded in detail. Not only does this provide a clear compliance trail, but it also ensures that if an audit or investigation ever comes up, you have the necessary documentation ready at hand.
Audit logs play a crucial role here, tracking system access and any interactions with PHI. These logs help detect unauthorized activity, demonstrate compliance, and provide insight into potential security risks before they escalate.
Good documentation means you are prepared, accountable, and proactive.

Even with airtight security measures, breaches can still happen. A stolen laptop, a phishing attack, or even an employee mistake — any of these could expose patient data. The difference between a disaster and a managed incident is a well-prepared response.
Your breach response plan should outline:
Think of a breach response plan as an emergency drill—practicing it ensures your team knows what to do when the time comes.
To make things easier, you can start by asking these questions.
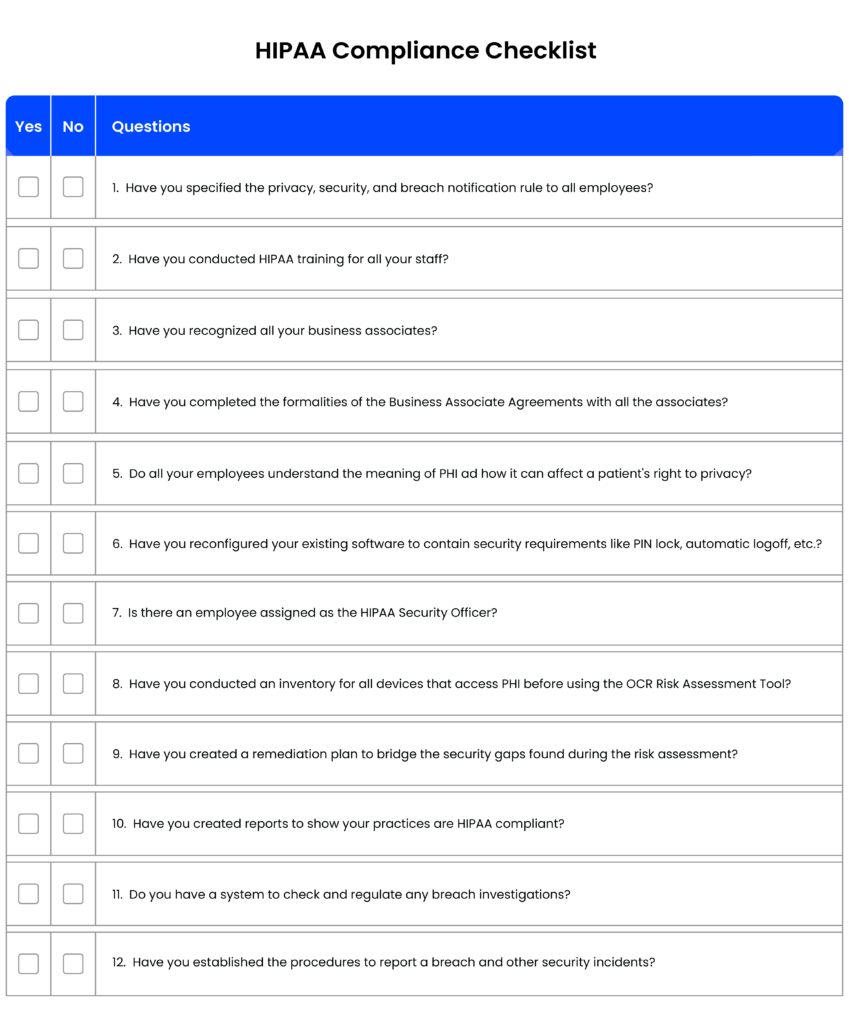
[You can also download the checklist to share it with your team: 12 Rule HIPAA Compliant Checklist]
With evolving regulations and the increasing complexity of healthcare data management, staying compliant can feel a weighted task.
But HIPAA compliance shouldn’t have to come at the cost of efficiency. The right tools can help healthcare organizations streamline patient interactions while ensuring every communication, record, and workflow meets HIPAA standards.
That’s where a HIPAA-compliant healthcare CRM like LeadSquared comes into the equation. It helps you securely manage patient data, automate communication, and more while maintaining compliance without the operational headaches.
Want to see how it works? Book a quick demo and find out how LeadSquared can simplify HIPAA compliance for your practice.
The HIPAA Security Rule sets forth the legal requirements for handling electronic protected health information (ePHI). It mandates healthcare providers to implement specific safeguards—administrative, physical, and technical—to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of ePHI. Compliance with the HIPAA Security Rule is crucial for protecting patient information and avoiding legal penalties.
HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) is a U.S. law that protects patient health information from being disclosed without consent. If you’re handling patient data—whether in a hospital, clinic, or private practice—you need to ensure that your systems, policies, and staff are following HIPAA guidelines. Non-compliance isn’t just a legal risk; it’s a patient trust issue.
HIPAA compliance has several moving parts, but the core elements include:
1. Privacy Rule – Governs how patient data can be used and shared.
2. Security Rule – Requires safeguards for electronic health data.
3. Breach Notification Rule – Mandates reporting of data breaches.
4. Administrative, Physical & Technical Safeguards – Covers staff training, facility security, and data encryption.
If you’re managing patient records, billing, or communications, all these rules apply to you.
It starts with a HIPAA compliance checklist that covers:
1. Conducting regular risk assessments
2. Implementing data encryption and secure access controls
3. Training employees on HIPAA policies
4. Having a clear breach response plan
5. Using HIPAA-compliant software for patient communication and data management
It’s not a one-and-done process. Compliance is ongoing and requires regular audits and updates.
Some of the most common slip-ups include:
1. Leaving patient records accessible to unauthorized staff
2. Sending unencrypted emails with sensitive patient information
3. Lack of employee training on handling patient data
4. Failing to report breaches within the required timeframe
Small mistakes can lead to hefty fines, so it’s crucial to have airtight policies.
Absolutely. Any communication containing Protected Health Information (PHI) must be HIPAA-compliant. That means:
1. No sending PHI via unencrypted emails
2. No discussing patient details over unsecured messaging apps
3. Using platforms that offer end-to-end encryption and access controls
This is where a HIPAA-compliant CRM can make life easier by ensuring all patient interactions are secure and trackable.
A HIPAA-compliant healthcare CRM like LeadSquared helps by:
1. Encrypting patient data to prevent unauthorized access
2. Automating compliance workflows for patient outreach, appointments, and follow-ups
3. Maintaining detailed audit logs to track access and communication history
4. Restricting user access based on roles to prevent data leaks
Basically, it acts as a safety net, ensuring every patient interaction follows HIPAA guidelines.
Not all CRMs are built for healthcare. If HIPAA compliance is a priority, look for:
1. End-to-end encryption for all patient data
2. Role-based access controls to limit who can view/edit records
3. Audit logs to track every action taken
4. Secure patient communication tools (email, SMS, portal)
5. Integration with EHRs for easy record-keeping
LeadSquared, for example, checks all these boxes—helping healthcare providers automate workflows while keeping compliance in check.
Fines, legal trouble, and damaged patient trust. HIPAA violations can lead to penalties ranging from $100 to $50,000 per violation, depending on severity. Repeated offenses? You could be looking at millions in fines. Worse, you risk losing your ability to handle patient data altogether.
Regular HIPAA audits are a must. Ideally, conduct an internal audit at least once a year and an external audit every 2–3 years. If there’s a security incident or policy change, update your compliance protocols immediately.