If you are new to the marketing world, then B2B vs. B2C sales might seem puzzling. Sure, they both talk about sales. But they can help you segregate your audience and shape your marketing strategy.
Yet, distinguishing between both sales models can be tricky. In some cases, they talk about similar products. For instance, fashion clothing manufacturers can be both B2B and B2C simultaneously. Manufacturers can sell private-label clothes to fashion houses. At the same time, they can still sell clothes to consumers directly.
Again, the marketing world is rife with ambiguous buzzwords and catchphrases like these. Therefore, you must learn to differentiate and use these words efficiently. It will help you communicate proper ideas to your peers and other external stakeholders.
So, in this article, we will share all you need to know about B2B vs B2C sales. The goal is to help you with several critical similarities and differences to help improve your sales techniques.
What is the difference between B2B and B2C?
The difference between B2B and B2C is that Business to Business (B2B) Sales refers to a sales model that targets businesses. Therefore, the term B2B describes business relationships between at least two firms. For example, LeadSquared is a B2B firm that sells CRM software to companies. Another example of a B2B business is Autoliv. They manufacture airbags for Ford and Toyota companies.
In contrast, B2C (Business-to-Consumer) refers to business relationships between companies and consumers. Taco Bell is a great example. As a popular fast-food restaurant, they sell delicious tacos and burritos to thousands of customers. Netflix is another excellent example of a B2C company. They create streaming entertainment for millions of people worldwide.
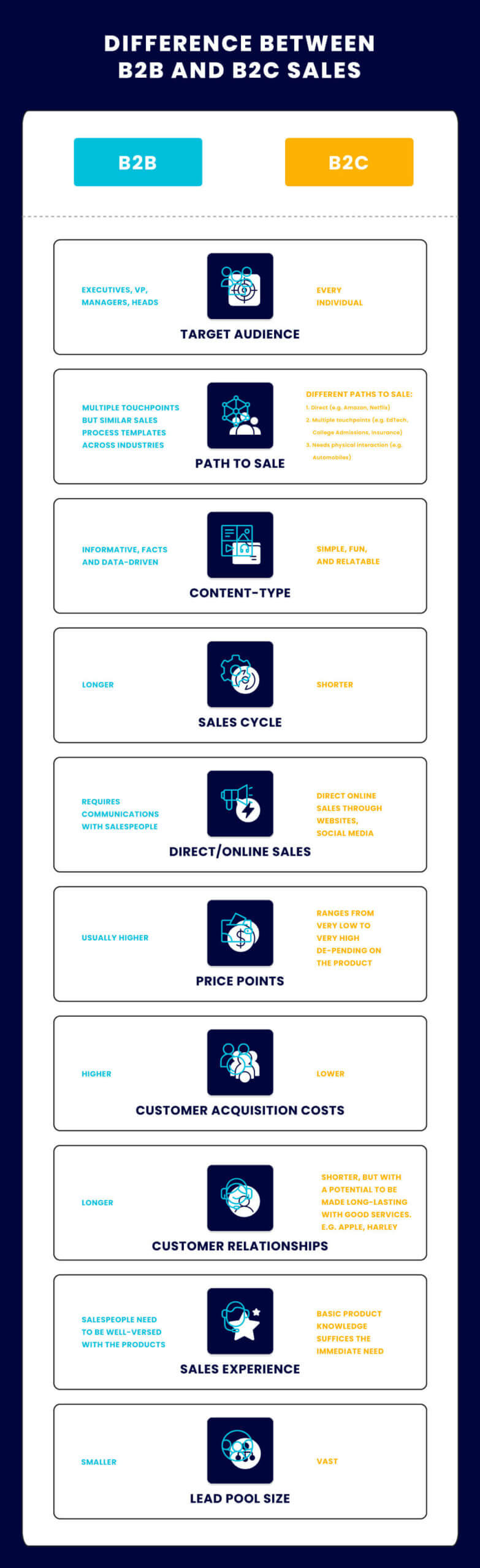
B2B vs B2C sales: 10 differences
1. Target audience
The most remarkable difference between B2C and B2B sales is the target audience.
Now, a person who is making a B2B purchase vs. a person who is making a B2C (personal) purchase might be the same one. But their motivations and the ways they behave in both scenarios may be poles apart. A person who is very “seemingly” rational in making a B2B purchase can be very illogical in making a personal purchase.
Therefore, based on the nature of the product you’re trying to sell, you need to identify professional and personal attributes.
For example, for B2B sales, the identifiable attributes of your target audience can be their professions. Here, you can pitch your products/services to high-level executives, managers, finance heads, IT heads, and other roles that fit your audience persona.
On the other hand, B2C buyer persona depends on their interests and affinity. For example, whether they are looking to travel, do they like luxury products, are they sensitive towards pricing, and demographics such as age, location, gender, etc.
Whether professional or personal, buyers will look for ways to get the best deals from salespeople. Therefore, strong negotiating skills and networking is the key here. For executives, shorter and punchier sales strategies with value prepositions are the go-to methods. While immediate benefits, discounts, social validation, etc., resonate more with B2C buyers.
2. Path to sale
B2B vs B2C sales process:
B2B buyers require more nurturing than B2C buyers. They need multiple contact points to build trust. B2B buyers make rational and strategic considerations. For instance, they will assess how a product or service can help their brand drive revenue. They will also measure how it generates value or achieves other concrete goals.
On the other hand, emotional attachments, personal gratification, and financial considerations drive B2C purchases. Therefore, you need to create lifestyle-based content to influence their purchase decisions. During awareness, B2C buyers focus on identifying the challenges they might face. In the consideration stage, they consider if a specific product meets their needs.
In other words, B2B sales requires multiple touchpoints but follow almost similar sales processes across industries. While the path of B2C sales can be:
- Direct purchase from websites or apps (for example, Amazon, Netflix, Taco Bell)
- Require multiple touchpoints, such as social, website, phone calls, etc. (for example, EdTech, College Admissions, Insurance sales)
- Needs physical interaction and trials (for example, buying automobiles)
3. Content-type
B2B buyers require educational content. They expect statistics, facts, and data to vet your product. Whitepapers and product demos are some resources they might use. On the other hand, B2C customers expect lifestyle-based content.
You will need simple, fun, and relatable content to win them. For instance, a brand like Apple sells by appealing to human emotions and sentiments. In contrast, brands like Mattermark create data-driven insights to help grow companies.
4. Sales cycle
B2B commerce involves a complex, steep, and multifaceted sales cycle. There will be many consultations, reviews, and evaluations before the sale occurs. You will have meetings with different people. It may include IT staff, managers, product users, and executives to make one sale.
Still, their decision is never finite but ongoing. B2B buyers will continuously review their decision to make sure it stays relevant. In contrast, B2C sales cycles are shorter. Your customer can even purchase from the first touchpoint.

5. Direct online sales
B2C customers usually buy from websites directly. But this seldom happens in B2B. For instance, let us talk about software products. Many B2B buyers can buy product/product subscriptions from the website. SaaS products like Amazon Web Services and Slack are great examples. Yet, B2B buyers need salespeople to pitch in, provide demos, and even make forecasts.
However, there can be some exceptions. For example, if we look at the B2C insurance industry, customers can buy insurance directly from insurance websites and marketplaces. They expect and will speak to the sales agents/representatives before their purchase.
6. Price points
In B2B, there may be several vendors driving each other’s prices up and down. However, in the case of B2C, there generally will be a standard below which one would not be able to get what they are looking for. Another fact is, B2B price points are usually higher than B2C. It is one reason B2B customers take time to evaluate before deciding.
On the contrary, the price points of B2C products may range from very low to very high. People buy lower price range products instantly. But when it comes to purchasing higher-value products, they seek more information and evaluate reviews. For instance, when a consumer wishes to buy a pair of shoes, they can instantly find the right one from the get-go. However, their need for more information increases if they want to purchase a new car.
7. Acquisition costs
In B2B sales, you might spend more acquiring a customer. Usually, the higher prices they pay justify the funds they spend on acquisition. There are also more opportunities to generate repeat sales over time.
B2C sales, on the other hand, usually have lower customer acquisition costs. Some customers can make purchases from word of mouth referrals, experiment with a new product, impulsive buying, etc. The smaller sales cycle in B2C also correlates with lower acquisition costs.
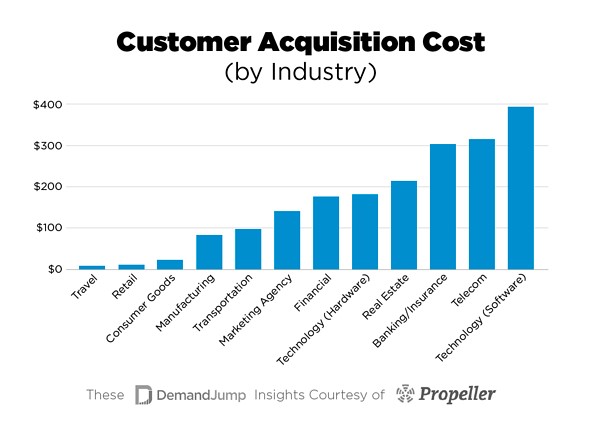
Median B2C and B2B acquisition cost across industries:
- Travel: $7
- Retail: $10
- Consumer Goods: $22
- Manufacturing: $83
- Transportation: $98
- Marketing Agency: $141
- Technology (Hardware): $182
- Real Estate: $213
- Banking/Insurance: $303
- Telecom: $315
- Technology (Software): $395
Source: DemandJump
8. Customer relationships
B2B buyers take more time to assess before purchasing. Therefore, they build stronger relationships with their vendors. Their relationships are also ongoing and will often require contact. However, a bad experience can ruin the relationship with your customer forever. There are possibilities that they may never return to make sales in the future.
Another problem that B2B buyers face (if they are not satisfied with the purchase) is long-term contracts and migration costs. Let’s say a business has purchased software, and after some time, management realizes that they are not able to get their ROI at all. That is when they start to think about making the switch. Many B2B companies get stuck in such forms of contracts and the overhead cost of migration. However, such practices don’t do any good to sellers because eventually, they will not only lose referrals but also have to deal with negative sentiments for their product in the industry. It would also drive up their service/support costs.
B2C, on the other hand, has a shorter customer relationship management cycle. For instance, you will not need intervention from the customer success team for every product you sell. B2C customers are also less loyal and only contact retail point-of-sale. Depending on their need, they may or may not return to buying your products or services.
9. Sales experience
B2B vs B2C sales experience: Your organizational sales policies will ultimately influence the skills you need to close more deals. While B2C salespeople have many years of experience, their learning and success curve is relatively short.
In contrast, B2B salespeople need to know the products they sell from the inside out. They must be able to provide in-depth information at the drop of the hat. B2B sales professionals may also need years to create the right sales strategy and personality to achieve results.
10. Lead pool size
The lead pool size is also a top B2B versus B2C sales differentiator. While B2Cs target millions of consumers at once, B2B has a narrower reach. For instance, Spotify targets millions of music lovers all over the world. Therefore, they curate content with the unique goal of reaching these numbers.
In contrast, brands like Ableton provide recording software for music professionals. If you compare the lead pool size for both companies, you will find that Ableton has a much smaller lead pool than Spotify.
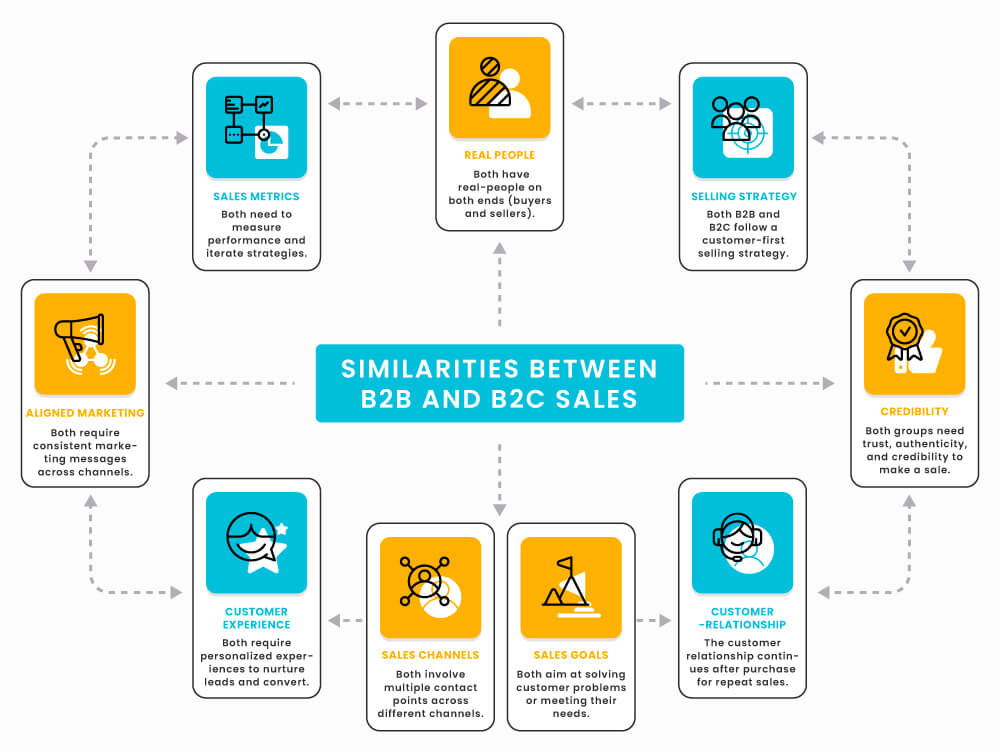
9 Similarities between B2B and B2C sales
1. Real people – Both sales models have real people on both ends, i.e., buyers and sellers.
2. Customer first – You need a grand customer-centric sales process. It includes exceptional support service and customer experience. You need to put your customers first to generate sales from both models.
3. Credibility – Both groups need trust, authenticity, and credibility to make a sale.
4. Customer journey – Both sales models do not end with the purchase. They continue long after for retention and repeat sales.
5. Goals – Both sales models still need you to solve your client’s problems. For this, you need to define your customer profiles, buyer’s journey, and buying personas. These will help you refine your sales strategy to achieve success.
6. Channels – Both groups require that you provide multiple contact points across different channels.
7. Experience – Both B2B and B2C sales require personalized experiences to nurture, engage, convert, and make sales.
8. Aligned marketing – Both groups require consistent and well-aligned marketing messages. It is essential for both online and offline communications. When messages don’t align, customers tend to move along to the next competitor.
9. Defined Strategy – Both B2B and B2C sales models need a clear strategy. It is crucial, even as B2B sales professionals take a longer time to convert. You need to have the clarity to measure performance, mitigate risks, and resolve issues effectively.
Key takeaways
B2C selling is different from selling to B2B customers, though they have a few similarities. But you should not see these differentiators as etched in stone. There will always be events where the general rules do not apply.
There are also brands making B2B and B2C sales at the same time, and on many occasions, they use the same sales channels.
One such brand doing both is Flexfire LEDs. While they make sales direct to consumers, 80% of their revenue comes from B2B sales. Overall, every business is unique. Therefore, it is up to you to figure out how to market your product or service.
FAQs
In terms of market, B2C is more profitable as you can sell a product to many different individuals. That is, you don’t have to spend on customizing products for every customer. However, the market price is fixed for every B2C product. So, your profit will depend a lot on the number of items sold.
The profit from B2B products depends on your clients and market share. Because of the higher ticket size, finding appropriate customers is a challenge and a blocker in making profits.
B2C and B2B sales strategies differ in terms of buyers, sales cycles, touchpoints, customer acquisition, cross-sell and upsell opportunities and the number of interactions with buyers.
B2C, or business-to-consumer, sales refer to transactions in which businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers. These sales typically take place in retail environments, online platforms, or any setting where the business interacts with individual customers. B2C sales can happen at retail stores, e-commerce websites, fast-food restaurants, travel and hospitality, etc.







