As a healthcare provider, automation is your ally in leading change. Automated technologies such as robotics process automation (RPA) or marketing automation help streamline key organizational processes—and can save a significant amount of money.
According to healthcare industry research organization CAQH, the industry has reduced administrative costs by $122 billion due to automation. By fully automating some common tasks, healthcare organizations could save an additional $16 billion.
What is automation in healthcare?
In the context of healthcare, automation is a range of technologies that reduce the need for human intervention in administrative and diagnostic processes. Automation improves organizational efficiency by limiting staff workload and potential errors, among other benefits.
One word of warning to healthcare leaders: Vendors sometimes claim products as automation, which isn’t fully the case. True automation will have one or more of the following attributes:
- Able to start, run and end without human intervention
- Runs in the background without attention
- Automatically performs a task or sequence of tasks
To automate, or not to automate?
Healthcare organizations typically perform many tasks which can benefit from automation, like scheduling appointments or waitlist management. As a rule of thumb, tasks with the following qualities are worth considering for automation:
- Time-consuming processes which are rarely completed
- High-effort, low-benefit tasks
- Existing best practices with outdated workflows
So, what are some specific ways automation can benefit healthcare—and which tools should leaders consider?
7 benefits of automation in healthcare
1. Simplified scheduling
Automation can help healthcare administrators schedule and manage appointments more efficiently. Automated systems can book appointments and send reminders via text, email, and phone, creating more time for staff to focus on patient care.
Other benefits include:
- Reduced risk of communication errors
- Fewer no-show appointments
- A convenient response format for patients
The following automation tools are commonly used in healthcare for simplified scheduling:
- CRM, such as LeadSquared’s HIPAA-compliant CRM
- Robotics process automation (RPA), like chatbots or voicebots
To learn more about how automation can help with scheduling—and best practices for drafting messages—check out 10 Ways to Reduce Patient No-Shows.
2. Improved patient communication
Automation can also help simplify and manage patient communication between appointments. Most marketing automation and CRM software offer email and SMS texting to help build patient relationships and field questions.
Automated SMS can be especially effective as a majority of patients want mobile interaction with providers, per a recent survey by Becker’s Health IT.
Healthcare managers can use texting for:
- Appointment reminders
- Follow-up care instructions
- Office notifications and updates
- Bill payment
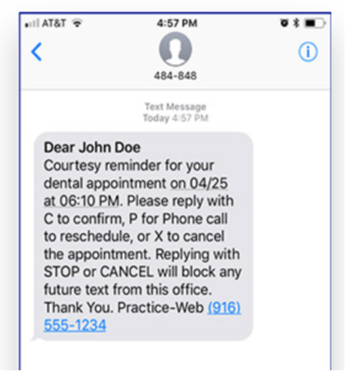
Check out this sample text from Practice-Web as an example of automation in action. Our 10 Ways to Reduce Patient No-Shows for more text examples and templates for messaging.
You might also consider adding a chatbot or other RPA technology to your website’s homepage. Chatbots offer other instant and convenient communication options which can:
- Answer simple questions
- Refer patients to further information sources
- Collect follow-up information
- Help staff triage patient care needs
3. Reduced workload—and lower costs
Healthcare managers can reduce staff workload with automation—a benefit that also lowers overhead costs. Using automation, staff can accomplish more in less time, allowing for higher quality patient care.
Other benefits include:
- Reduced work hours
- Improved efficiency
- Fewer task errors
- Lower stress levels
Several administrative areas are perfect for automation. Practice managers might consider automating processes for:
- Billing
- Insurance claims
- Selecting and confirming medical codes
- Onboarding and training
4. Easier access to data
Consider utilizing automation to access and transfer patient data. Many CRMs include a core systems integration, which organizes electronic health records (EHRs) for efficient data exchange among departments, facilities and devices.
“Siloed information is one of the biggest internal challenges that ultimately affects the quality of the service provided. To improve productivity, healthcare providers need to consolidate multiple disparate data sources and systems into a single source of truth about the patient.”
Automation in Healthcare: The Key to Unlock Innovation” by Persistent
Additional benefits include:
- Improved treatment flow
- Reduced administrative overhead
- Faster data retrieval
- Reduced risk of error
Automation can also help improve decision-making, providing valuable insight into patient needs and behavior. Automated systems can scan EHRs for details on patients’:
- Demographics
- Treatment goals
- History and background
5. Ensures HIPAA compliance
As you know, HIPAA compliance is a non-negotiable for healthcare organizations. Automation can help ensure compliance by configuring data usage rights—a function that grants access only to authorized personnel.
Automation tools like LeadSquared’s HIPAA-compliant CRM protect patient data by:
- Maintaining Protected Health Information (PHI) security
- Meeting industry requirements for data protection
“If a consumer takes a medical exam or has a blood analysis, that consumer expects personal information to remain secure and the results to be accurate. Once again, healthcare providers can take advantage of software to control who accesses the patient’s personal data and ensure they deliver error-free results.”
Automation in Healthcare: The Key to Unlock Innovation, by Persistent
To ensure data is reliably secure, consider prioritizing HIPAA-compliant automation tools. Tools might include:
- CRM software
- Chat messaging
- Patient engagement platforms
- Email marketing software (via marketing automation)
6. Limit errors
According to National Center for Biotechnology Information, about 400,000 hospital patients experience some type of preventable harm each year, with medical errors costing up to $20 billion annually. Automation can enable more effective care—and cost savings—by reducing the risk of human error.
Healthcare providers and managers can use automated tools to improve:
- Patient diagnosis and treatment
- Administrative operations (as in examples above)
For diagnosis and treatment, automated tools might include:
- Wearable medical devices, like blood pressure monitors
- Smartwatches, which track fitness and sleep
- Biosensors, for respiratory rate and temperature data
The automated insulin delivery system is a particularly illustrative example. Approved by the FDA in 2020, the system monitors glucose levels for pediatric diabetes patients and automatically provides appropriate insulin doses. The automated system limits risk of treatment error by dispensing insulin based on real-time data—and reduces strain on caregivers.
7. Improved emergency management
Automation can help healthcare managers respond more quickly and effectively during emergencies. The Covid-19 pandemic is a prime example.
During the pandemic, healthcare organizations leveraged automation to help:
- Reduce testing wait times
- Analyze incoming data
- Automate reporting
- Accelerate recruiting and hiring staff
Software company UiPath cites robotic process automation as a particularly effective emergency management tool. UiPath leveraged RPA to expedite Covid-19 test results, also helping innovate slow or outdated healthcare systems.
In one case, implementing RPA saved staff up to three hours a day by:
- Eliminating manual data entry
- Accelerating operational efficiencies
- Improving employee experience
Address implementation challenges
Healthcare practice leaders may need to address several key challenges when implementing automation technologies. Consider mitigating the following points during the automation adoption process.
Job security concerns
Staff may fear automation will eliminate jobs. Studies show automation actually does the opposite, helping improve jobs by reducing mundane administrative tasks. Schedule training to reassure employees and ensure the staff understands how to use technologies.
Mistrust from patients
Patients—as well as some healthcare providers—may not trust automated treatment plans. Consider distributing materials on the benefits of automated treatment to assuage concerns. You might consider including links to articles in emails to patients or providing handouts at appointments.
Cost concerns
Automation can be expensive to adopt and implement, garnering skepticism from staff. Be sure to emphasize the ROI of automation—especially in terms of long-term costs and reduced staff workloads.
Automation can help innovate healthcare through improved processes, cost savings, and elevated patient satisfaction.







